Diverse responses to UV light exposure in Acinetobacter include the capacity for DNA damage-induced mutagenesis in the opportunistic pathogens Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter ursingii
- PMID: 22117008
- PMCID: PMC3352118
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.054668-0
Diverse responses to UV light exposure in Acinetobacter include the capacity for DNA damage-induced mutagenesis in the opportunistic pathogens Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter ursingii
Abstract
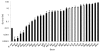
Error-prone and error-free DNA damage repair responses that are induced in most bacteria after exposure to various chemicals, antibiotics or radiation sources were surveyed across the genus Acinetobacter. The error-prone SOS mutagenesis response occurs when DNA damage induces a cell's umuDC- or dinP-encoded error-prone polymerases. The model strain Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 possesses an unusual, regulatory umuD allele (umuDAb) with an extended 5' region and only incomplete fragments of umuC. Diverse Acinetobacter species were investigated for the presence of umuDC and their ability to conduct UV-induced mutagenesis. Unlike ADP1, most Acinetobacter strains possessed multiple umuDC loci containing either umuDAb or a umuD allele resembling that of Escherichia coli. The nearly omnipresent umuDAb allele was the ancestral umuD in Acinetobacter, with horizontal gene transfer accounting for over half of the umuDC operons. Despite multiple umuD(Ab)C operons in many strains, only three species conducted UV-induced mutagenesis: Acinetobacter baumannii, Acinetobacter ursingii and Acinetobacter beijerinckii. The type of umuDC locus or mutagenesis phenotype a strain possessed was not correlated with its error-free response of survival after UV exposure, but similar diversity was apparent. The survival of 30 Acinetobacter strains after UV treatment ranged over five orders of magnitude, with the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-A. baumannii (Acb) complex and haemolytic strains having lower survival than non-Acb or non-haemolytic strains. These observations demonstrate that a genus can possess a range of DNA damage response mechanisms, and suggest that DNA damage-induced mutation could be an important part of the evolution of the emerging pathogens A. baumannii and A. ursingii.
Figures


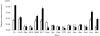
Similar articles
-
A constitutively expressed, truncated umuDC operon regulates the recA-dependent DNA damage induction of a gene in Acinetobacter baylyi strain ADP1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Jun;72(6):4036-43. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02774-05. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16751513 Free PMC article.
-
The DdrR Coregulator of the Acinetobacter baumannii Mutagenic DNA Damage Response Potentiates UmuDAb Repression of Error-Prone Polymerases.J Bacteriol. 2022 Nov 15;204(11):e0016522. doi: 10.1128/jb.00165-22. Epub 2022 Oct 4. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 36194009 Free PMC article.
-
UmuDAb: An Error-Prone Polymerase Accessory Homolog Whose N-Terminal Domain Is Required for Repression of DNA Damage Inducible Gene Expression in Acinetobacter baylyi.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 24;11(3):e0152013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152013. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27010837 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analyses of cellular functions required for UV mutagenesis in Escherichia coli.Basic Life Sci. 1990;52:269-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9561-8_22. Basic Life Sci. 1990. PMID: 2183772 Review.
-
A new model for SOS-induced mutagenesis: how RecA protein activates DNA polymerase V.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Jun;45(3):171-84. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.480968. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20441441 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial sweeteners stimulate horizontal transfer of extracellular antibiotic resistance genes through natural transformation.ISME J. 2022 Feb;16(2):543-554. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01095-6. Epub 2021 Sep 1. ISME J. 2022. PMID: 34465899 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in gene expression of recA and umuDC in antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.J Med Life. 2023 Apr;16(4):531-539. doi: 10.25122/jml-2022-0358. J Med Life. 2023. PMID: 37305826 Free PMC article.
-
Global transcriptome and physiological responses of Acinetobacter oleivorans DR1 exposed to distinct classes of antibiotics.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 17;9(10):e110215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110215. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25330344 Free PMC article.
-
A genomic island integrated into recA of Vibrio cholerae contains a divergent recA and provides multi-pathway protection from DNA damage.Environ Microbiol. 2015 Apr;17(4):1090-102. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12512. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 24889424 Free PMC article.
-
The Small DdrR Protein Directly Interacts with the UmuDAb Regulator of the Mutagenic DNA Damage Response in Acinetobacter baumannii.J Bacteriol. 2022 Mar 15;204(3):e0060121. doi: 10.1128/jb.00601-21. Epub 2022 Feb 22. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35191762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbe V., Vallenet D., Fonknechten N., Kreimeyer A., Oztas S., Labarre L., Cruveiller S., Robert C., Duprat S. & other authors (2004). Unique features revealed by the genome sequence of Acinetobacter sp. ADP1, a versatile and naturally transformation competent bacterium. Nucleic Acids Res 32, 5766–5779. 10.1093/nar/gkh910 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berenstein D. (1987). UV-inducible DNA repair in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Mutat Res 183, 219–224. - PubMed
-
- Campoy S., Mazón G., Fernández de Henestrosa A. R., Llagostera M., Monteiro P. B., Barbé J. (2002). A new regulatory DNA motif of the gamma subclass Proteobacteria: identification of the LexA protein binding site of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Microbiology 148, 3583–3597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

