A novel pathway for human endothelial cell activation by antiphospholipid/anti-β2 glycoprotein I antibodies
- PMID: 22106343
- PMCID: PMC3265208
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-344671
A novel pathway for human endothelial cell activation by antiphospholipid/anti-β2 glycoprotein I antibodies
Abstract
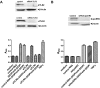
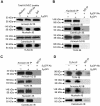
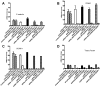
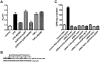
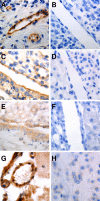
Antiphospholipid Abs (APLAs) are associated with thrombosis and recurrent fetal loss. These Abs are primarily directed against phospholipid-binding proteins, particularly β(2)GPI, and activate endothelial cells (ECs) in a β(2)GPI-dependent manner after binding of β(2)GPI to EC annexin A2. Because annexin A2 is not a transmembrane protein, the mechanisms of APLA/anti-β(2)GPI Ab-mediated EC activation are uncertain, although a role for a TLR4/myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent pathway leading to activation of NF-κB has been proposed. In the present study, we confirm a critical role for TLR4 in anti-β(2)GPI Ab-mediated EC activation and demonstrate that signaling through TLR4 is mediated through the assembly of a multiprotein signaling complex on the EC surface that includes annexin A2, TLR4, calreticulin, and nucleolin. An essential role for each of these proteins in cell activation is suggested by the fact that inhibiting the expression of each using specific siRNAs blocked EC activation mediated by APLAs/anti-β(2)GPI Abs. These results provide new evidence for novel protein-protein interactions on ECs that may contribute to EC activation and the pathogenesis of APLA/anti-β(2)GPI-associated thrombosis and suggest potential new targets for therapeutic intervention in antiphospholipid syndrome.
Figures
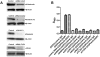
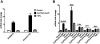
Similar articles
-
A novel pathway of cellular activation mediated by antiphospholipid antibody-induced extracellular vesicles.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Oct;13(10):1928-40. doi: 10.1111/jth.13072. Epub 2015 Sep 15. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 26264622 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin A2: biology and relevance to the antiphospholipid syndrome.Lupus. 2008 Oct;17(10):943-51. doi: 10.1177/0961203308095329. Lupus. 2008. PMID: 18827060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies induce monocyte release of tumor necrosis factor alpha and tissue factor by signal transduction pathways involving lipid rafts.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Aug;56(8):2687-97. doi: 10.1002/art.22802. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17665396
-
Anti-β(2)GPI/β(2)GPI induced TF and TNF-α expression in monocytes involving both TLR4/MyD88 and TLR4/TRIF signaling pathways.Mol Immunol. 2013 Mar;53(3):246-54. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.08.012. Epub 2012 Sep 8. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22964479
-
The role of TLR4 in pathophysiology of antiphospholipid syndrome-associated thrombosis and pregnancy morbidity.Br J Haematol. 2014 Jan;164(2):165-76. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12587. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Br J Haematol. 2014. PMID: 24180619 Review.
Cited by
-
The journey of antiphospholipid antibodies from cellular activation to antiphospholipid syndrome.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015 Mar;17(3):16. doi: 10.1007/s11926-014-0485-9. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25761923 Review.
-
The pathogenesis of obstetric APS: a 2023 update.Clin Immunol. 2023 Oct;255:109745. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109745. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37625670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogen recognition receptor crosstalk in respiratory syncytial virus sensing: a host and cell type perspective.Trends Microbiol. 2013 Nov;21(11):568-74. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Trends Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24119913 Free PMC article.
-
Release of neutrophil extracellular traps by neutrophils stimulated with antiphospholipid antibodies: a newly identified mechanism of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Nov;67(11):2990-3003. doi: 10.1002/art.39247. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26097119 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-Contained APOH Associated With Antiphospholipid Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2021 May 4;12:604222. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.604222. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34040601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rand JH. The antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rev Med. 2003;54:409–424. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Irastorza G, Crowther M, Branch W, Khamashta MA. Antiphospholipid syndrome. Lancet. 2010;376(9751):1498–1509. - PubMed
-
- Pierangeli SS, Chen PP, Raschi E, et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome: pathogenic mechanisms. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2008;34(3):236–250. - PubMed
-
- Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Shoenfeld Y, et al. Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 5-year period: a multicentre prospective study of 1000 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:1428–1432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

