Direct, noncatalytic mechanism of IKK inhibition by A20
- PMID: 22099304
- PMCID: PMC3237303
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.09.015
Direct, noncatalytic mechanism of IKK inhibition by A20
Abstract
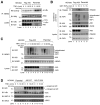
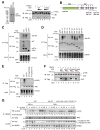
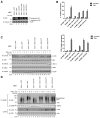
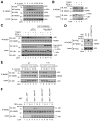
A20 is a potent anti-inflammatory protein that inhibits NF-κB, and A20 dysfunction is associated with autoimmunity and B cell lymphoma. A20 harbors a deubiquitination enzyme domain and can employ multiple mechanisms to antagonize ubiquitination upstream of NEMO, a regulatory subunit of the IκB kinase complex (IKK). However, direct evidence of IKK inhibition by A20 is lacking, and the inhibitory mechanism remains poorly understood. Here we show that A20 can directly impair IKK activation without deubiquitination or impairment of ubiquitination enzymes. We find that polyubiquitin binding by A20, which is largely dependent on A20's seventh zinc-finger motif (ZnF7), induces specific binding to NEMO. Remarkably, this ubiquitin-induced recruitment of A20 to NEMO is sufficient to block IKK phosphorylation by its upstream kinase TAK1. Our results suggest a noncatalytic mechanism of IKK inhibition by A20 and a means by which polyubiquitin chains can specify a signaling outcome.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
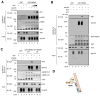
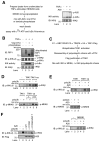
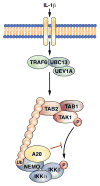
Comment in
-
A20: more than one way to skin a cat.Mol Cell. 2011 Nov 18;44(4):511-2. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.004. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 22099299
Similar articles
-
Specific recognition of linear polyubiquitin by A20 zinc finger 7 is involved in NF-κB regulation.EMBO J. 2012 Oct 3;31(19):3856-70. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.241. Epub 2012 Aug 28. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 23032187 Free PMC article.
-
A20 inhibits LUBAC-mediated NF-κB activation by binding linear polyubiquitin chains via its zinc finger 7.EMBO J. 2012 Oct 3;31(19):3845-55. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.240. Epub 2012 Aug 28. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 23032186 Free PMC article.
-
ATM- and NEMO-dependent ELKS ubiquitination coordinates TAK1-mediated IKK activation in response to genotoxic stress.Mol Cell. 2010 Oct 8;40(1):75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.010. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20932476 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, biological activities and mechanisms of action of A20 (TNFAIP3).Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;80(12):2009-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.044. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599425 Review.
-
A20-mediated negative regulation of canonical NF-κB signaling pathway.Immunol Res. 2013 Dec;57(1-3):166-71. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8463-2. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 24242761 Review.
Cited by
-
The deubiquitinase A20 mediates feedback inhibition of interleukin-17 receptor signaling.Sci Signal. 2013 Jun 4;6(278):ra44. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003699. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23737552 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ester-linked ubiquitylation sites during TLR7 signalling increases the number of inter-ubiquitin linkages from 8 to 12.Biochem J. 2022 Dec 9;479(23):2419-2431. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20220510. Biochem J. 2022. PMID: 36408944 Free PMC article.
-
Two phases of inflammatory mediator production defined by the study of IRAK2 and IRAK1 knock-in mice.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 1;191(5):2717-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203268. Epub 2013 Aug 5. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23918981 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin E δ-tocotrienol inhibits TNF-α-stimulated NF-κB activation by up-regulation of anti-inflammatory A20 via modulation of sphingolipid including elevation of intracellular dihydroceramides.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Feb;64:101-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.10.013. Epub 2018 Nov 3. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30471562 Free PMC article.
-
Haploinsufficiency of A20 impairs protein-protein interactome and leads into caspase-8-dependent enhancement of NLRP3 inflammasome activation.RMD Open. 2018 Oct 17;4(2):e000740. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000740. eCollection 2018. RMD Open. 2018. PMID: 30402268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianchi K, Meier P. A tangled web of ubiquitin chains: breaking news in TNF-R1 signaling. Mol Cell. 2009;36:736–742. - PubMed
-
- Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC, Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:1052–1060. - PubMed
-
- Bosanac I, Wertz IE, Pan B, Yu C, Kusam S, Lam C, Phu L, Phung Q, Maurer B, Arnott D, et al. Ubiquitin Binding to A20 ZnF4 Is Required for Modulation of NF-kappaB Signaling. Mol Cell. 2010;40:548–557. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZJ, Sun LJ. Nonproteolytic functions of ubiquitin in cell signaling. Mol Cell. 2009;33:275–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

