Rosmarinic acid and baicalin epigenetically derepress peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor γ in hepatic stellate cells for their antifibrotic effect
- PMID: 22095555
- PMCID: PMC3302956
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24792
Rosmarinic acid and baicalin epigenetically derepress peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor γ in hepatic stellate cells for their antifibrotic effect
Abstract
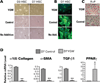
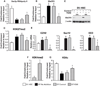
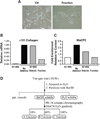
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) undergo myofibroblastic transdifferentiation (activation) to participate in liver fibrosis and identification of molecular targets for this cell fate regulation is essential for development of efficacious therapeutic modalities for the disease. Peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) is required for differentiation of HSCs and its epigenetic repression underlies HSC activation. The herbal prescription Yang-Gan-Wan (YGW) prevents liver fibrosis, but its active ingredients and molecular mechanisms are unknown. Here we demonstrate YGW prevents and reverses HSC activation by way of epigenetic derepression of Pparγ involving reductions in MeCP2 expression and its recruitment to Pparγ promoter, suppressed expression of PRC2 methyltransferase EZH2, and consequent reduction of H2K27di-methylation at the 3' exon. High-performance liquid chromatography / mass spectrometry (HPLC/MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyses identify polyphenolic rosmarinic acid (RA) and baicalin (BC) as active phytocompounds. RA and BC suppress the expression and signaling by canonical Wnts, which are implicated in the aforementioned Pparγ epigenetic repression. RA treatment in mice with existing cholestatic liver fibrosis inhibits HSC activation and progression of liver fibrosis.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate a therapeutic potential of YGW and its active component RA and BC for liver fibrosis by way of Pparγ derepression mediated by suppression of canonical Wnt signaling in HSCs.
Copyright © 2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ as a therapeutic target for hepatic fibrosis: from bench to bedside.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jan;70(2):259-76. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1046-x. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22699820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Necdin-Wnt pathway causes epigenetic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma repression in hepatic stellate cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):30463-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.156703. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20663865 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling in liver fibrosis: progress, challenges and potential directions.Biochimie. 2013 Dec;95(12):2326-35. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 24036368 Review.
-
Hepatic stellate cell-derived delta-like homolog 1 (DLK1) protein in liver regeneration.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):10355-10367. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.312751. Epub 2012 Feb 1. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22298767 Free PMC article.
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor 34-mer peptide prevents liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation through down-regulation of the PDGF receptor.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 24;9(4):e95443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095443. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24763086 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ as a therapeutic target for hepatic fibrosis: from bench to bedside.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jan;70(2):259-76. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1046-x. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22699820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Modifications in NAFLD: Mechanisms and Potential Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 27;24(19):14653. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914653. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curdione and Schisandrin C Synergistically Reverse Hepatic Fibrosis via Modulating the TGF-β Pathway and Inhibiting Oxidative Stress.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 10;9:763864. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.763864. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34858986 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Profiling Uncover the Underlying Mechanism of Color Differentiation in Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Flowers.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 9;13:884957. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.884957. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35755689 Free PMC article.
-
The Combination of Schisandrol B and Wedelolactone Synergistically Reverses Hepatic Fibrosis Via Modulating Multiple Signaling Pathways in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 3;12:655531. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.655531. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34149411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cassiman D, Barlow A, Vander BS, Libbrecht L, Pachnis V. Hepatic stellate cells do not derive from the neural crest. J Hepatol. 2006 Jun;44(6):1098–1104. - PubMed
-
- Geerts A. History, heterogeneity, developmental biology, and functions of quiescent hepatic stellate cells. Semin Liver Dis. 2001 Aug;21(3):311–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AA018663-01/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P50AA11199/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA018663/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA020753-01/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AA012885/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AA012885-10/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01AA020753/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA020753/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AA018663/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R24AA12885/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
