Structural analysis of an eIF3 subcomplex reveals conserved interactions required for a stable and proper translation pre-initiation complex assembly
- PMID: 22090426
- PMCID: PMC3300007
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr765
Structural analysis of an eIF3 subcomplex reveals conserved interactions required for a stable and proper translation pre-initiation complex assembly
Abstract
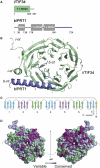
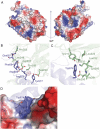
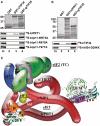
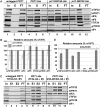
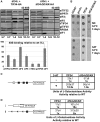
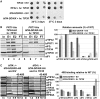
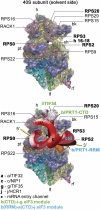
Translation initiation factor eIF3 acts as the key orchestrator of the canonical initiation pathway in eukaryotes, yet its structure is greatly unexplored. We report the 2.2 Å resolution crystal structure of the complex between the yeast seven-bladed β-propeller eIF3i/TIF34 and a C-terminal α-helix of eIF3b/PRT1, which reveals universally conserved interactions. Mutating these interactions displays severe growth defects and eliminates association of eIF3i/TIF34 and strikingly also eIF3g/TIF35 with eIF3 and 40S subunits in vivo. Unexpectedly, 40S-association of the remaining eIF3 subcomplex and eIF5 is likewise destabilized resulting in formation of aberrant pre-initiation complexes (PICs) containing eIF2 and eIF1, which critically compromises scanning arrest on mRNA at its AUG start codon suggesting that the contacts between mRNA and ribosomal decoding site are impaired. Remarkably, overexpression of eIF3g/TIF35 suppresses the leaky scanning and growth defects most probably by preventing these aberrant PICs to form. Leaky scanning is also partially suppressed by eIF1, one of the key regulators of AUG recognition, and its mutant sui1(G107R) but the mechanism differs. We conclude that the C-terminus of eIF3b/PRT1 orchestrates co-operative recruitment of eIF3i/TIF34 and eIF3g/TIF35 to the 40S subunit for a stable and proper assembly of 48S pre-initiation complexes necessary for stringent AUG recognition on mRNAs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The RNA recognition motif of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3g (eIF3g) is required for resumption of scanning of posttermination ribosomes for reinitiation on GCN4 and together with eIF3i stimulates linear scanning.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;30(19):4671-86. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00430-10. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20679478 Free PMC article.
-
The indispensable N-terminal half of eIF3j/HCR1 cooperates with its structurally conserved binding partner eIF3b/PRT1-RRM and with eIF1A in stringent AUG selection.J Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 5;396(4):1097-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.047. Epub 2010 Jan 11. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20060839 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the RNP1 motif in PRT1 with HCR1 promotes 40S binding of eukaryotic initiation factor 3 in yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):2984-98. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.2984-2998.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581774 Free PMC article.
-
eIF3: a versatile scaffold for translation initiation complexes.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Oct;31(10):553-62. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.08.005. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16920360 Review.
-
The scanning mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:779-812. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035802. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24499181 Review.
Cited by
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 plays distinct roles at the mRNA entry and exit channels of the ribosomal preinitiation complex.Elife. 2016 Oct 26;5:e20934. doi: 10.7554/eLife.20934. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27782884 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the mammalian ribosomal 43S preinitiation complex bound to the scanning factor DHX29.Cell. 2013 May 23;153(5):1108-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.036. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23706745 Free PMC article.
-
'Ribozoomin'--translation initiation from the perspective of the ribosome-bound eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs).Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Jun;13(4):305-30. doi: 10.2174/138920312801619385. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22708493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3B downregulation inhibits cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis through negatively regulating tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 21 in gastric cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Oct;8(6):2242-2251. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.09.42. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116977 Free PMC article.
-
Novel RNA-binding protein P311 binds eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit b (eIF3b) to promote translation of transforming growth factor β1-3 (TGF-β1-3).J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 5;289(49):33971-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.609495. Epub 2014 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25336651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hinnebusch AG. eIF3: a versatile scaffold for translation initiation complexes. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:553–562. - PubMed
-
- Cuchalová L, Kouba T, Herrmannová A, Danyi I, Chiu W-l, Valášek L. The RNA recognition motif of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3g (eIF3g) is required for resumption of scanning of posttermination ribosomes for reinitiation on GCN4 and together with eIF3i stimulates linear scanning. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010;30:4671–4686. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

