Effects of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange (BIG) 1 and KANK1 proteins on cell polarity and directed migration during wound healing
- PMID: 22084092
- PMCID: PMC3228443
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1117011108
Effects of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange (BIG) 1 and KANK1 proteins on cell polarity and directed migration during wound healing
Abstract
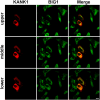
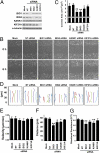
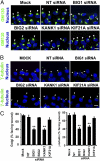
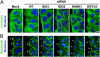
Brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein (BIG) 1 activates class I ADP ribosylation factors (ARFs) by accelerating the replacement of bound GDP with GTP to initiate recruitment of coat proteins for membrane vesicle formation. Among proteins that interact with BIG1, kinesin family member 21A (KIF21A), a plus-end-directed motor protein, moves cargo away from the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) on microtubules. Because KANK1, a protein containing N-terminal KN, C-terminal ankyrin-repeat, and intervening coiled-coil domains, has multiple actions in cells and also interacts with KIF21A, we explored a possible interaction between it and BIG1. We obtained evidence for a functional and physical association between these proteins, and found that the effects of BIG1 and KANK1 depletion on cell migration in wound-healing assays were remarkably similar. Treatment of cells with BIG1- or KANK1-specific siRNA interfered significantly with directed cell migration and initial orientation of Golgi/MTOC toward the leading edge, which was not mimicked by KIF21A depletion. Although colocalization of overexpressed KANK1 and endogenous BIG1 in HeLa cells was not clear microscopically, their reciprocal immunoprecipitation (IP) is compatible with the presence of small percentages of each protein in the same complexes. Depletion or overexpression of BIG1 protein appeared not to affect KANK1 distribution. Our data identify actions of both BIG1 and KANK1 in regulating cell polarity during directed migration; these actions are consistent with the presence of both BIG1 and KANK1 in dynamic multimolecular complexes that maintain Golgi/MTOC orientation, differ from those that might contain all three proteins (BIG1, KIF21A, and KANK1), and function in directed transport along microtubules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein (BIG) 1 and kinesin motor protein KIF21A.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 2;105(48):18788-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810104105. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19020088 Free PMC article.
-
Arf guanine nucleotide-exchange factors BIG1 and BIG2 regulate nonmuscle myosin IIA activity by anchoring myosin phosphatase complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 20;110(34):E3162-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312531110. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23918382 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analyses of key features in the KANK1·KIF21A complex yield mechanistic insights into the cross-talk between microtubules and the cell cortex.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 5;293(1):215-225. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.816017. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29158259 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating the regulators: role of phosphorylation in modulating the function of the GBF1/BIG family of Sec7 ARF-GEFs.FEBS Lett. 2020 Jul;594(14):2213-2226. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13798. Epub 2020 May 14. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 32333796 Review.
-
Activation of toxin ADP-ribosyltransferases by eukaryotic ADP-ribosylation factors.Mol Cell Biochem. 1999 Mar;193(1-2):153-7. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10331652 Review.
Cited by
-
Kank1 reexpression induced by 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Feb 1;8(2):1658-65. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25973051 Free PMC article.
-
KANK2 Links αVβ5 Focal Adhesions to Microtubules and Regulates Sensitivity to Microtubule Poisons and Cell Migration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Mar 3;8:125. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00125. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32195252 Free PMC article.
-
Kank Is an EB1 interacting protein that localises to muscle-tendon attachment sites in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 9;9(9):e106112. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106112. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25203404 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Role of KANK1 in Podocyte Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 27;25(11):5808. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115808. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891998 Free PMC article.
-
BIG1 is required for the survival of deep layer neurons, neuronal polarity, and the formation of axonal tracts between the thalamus and neocortex in developing brain.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 17;12(4):e0175888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175888. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28414797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ridley AJ, et al. Cell migration: Integrating signals from front to back. Science. 2003;302:1704–1709. - PubMed
-
- Raftopoulou M, Hall A. Cell migration: Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev Biol. 2004;265:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Weijer CJ. Collective cell migration in development. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3215–3223. - PubMed
-
- Etienne-Manneville S. Cdc42—the centre of polarity. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:1291–1300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

