CX3CR1 deficiency leads to impairment of hippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 22072675
- PMCID: PMC3236509
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3667-11.2011
CX3CR1 deficiency leads to impairment of hippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity
Abstract
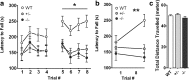
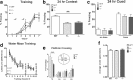
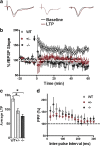
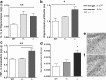
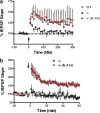
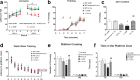
The protective/neurotoxic role of fractalkine (CX3CL1) and its receptor CX3C chemokine receptor 1 (CX3CR1) signaling in neurodegenerative disease is an intricate and highly debated research topic and it is becoming even more complicated as new studies reveal discordant results. It appears that the CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis plays a direct role in neurodegeneration and/or neuroprotection depending on the CNS insult. However, all the above studies focused on the role of CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling in pathological conditions, ignoring the relevance of CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling under physiological conditions. No approach to date has been taken to decipher the significance of defects in CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling in physiological condition. In the present study we used CX3CR1⁻/⁻, CX3CR1⁺/⁻, and wild-type mice to investigate the physiological role of CX3CR1 receptor in cognition and synaptic plasticity. Our results demonstrate for the first time that mice lacking the CX3CR1 receptor show contextual fear conditioning and Morris water maze deficits. CX3CR1 deficiency also affects motor learning. Importantly, mice lacking the receptor have a significant impairment in long-term potentiation (LTP). Infusion with IL-1β receptor antagonist significantly reversed the deficit in cognitive function and impairment in LTP. Our results reveal that under physiological conditions, disruption in CX3CL1 signaling will lead to impairment in cognitive function and synaptic plasticity via increased action of IL-1β.
Figures
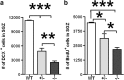
Similar articles
-
Involvement of CX3CL1/CX3CR1 in depression and cognitive impairment induced by chronic unpredictable stress and relevant underlying mechanism.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Mar 2;381:112371. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112371. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31765724
-
Phospholipase d2 ablation ameliorates Alzheimer's disease-linked synaptic dysfunction and cognitive deficits.J Neurosci. 2010 Dec 8;30(49):16419-28. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3317-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21147981 Free PMC article.
-
PI3Kγ is required for NMDA receptor-dependent long-term depression and behavioral flexibility.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Oct 23;14(11):1447-54. doi: 10.1038/nn.2937. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22019731
-
Chemokine CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) Signaling and Diabetic Encephalopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7527. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147527. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating neurotoxicity through CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Aug 8;8:229. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00229. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25152714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microglia, seen from the CX3CR1 angle.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Mar 18;7:26. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00026. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23507975 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of nonhematopoietic cells and mediators to immune responses: implications for immunotoxicology.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Jun;145(2):214-32. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv060. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26008184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothalamic Microglial Heterogeneity and Signature under High Fat Diet-Induced Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 24;22(5):2256. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052256. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythrocyte adenosine A2B receptor prevents cognitive and auditory dysfunction by promoting hypoxic and metabolic reprogramming.PLoS Biol. 2021 Jun 17;19(6):e3001239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001239. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2021. PMID: 34138843 Free PMC article.
-
The ischemic environment drives microglia and macrophage function.Front Neurol. 2015 Apr 8;6:81. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00081. eCollection 2015. Front Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25904895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aloisi F. Immune function of microglia. Glia. 2001;36:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Batchelor PE, Liberatore GT, Wong JY, Porritt MJ, Frerichs F, Donnan GA, Howells DW. Activated macrophages and microglia induce dopaminergic sprouting in the injured striatum and express brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosci. 1999;19:1708–1716. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bazan JF, Bacon KB, Hardiman G, Wang W, Soo K, Rossi D, Greaves DR, Zlotnik A, Schall TJ. A new class of membrane-bound chemokine with a CX3C motif. Nature. 1997;385:640–644. - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Weeber EJ, Durudas A, Qiu S, Masiulis I, Sweatt JD, Li WP, Adelmann G, Frotscher M, Hammer RE, Herz J. Modulation of synaptic plasticity and memory by Reelin involves differential splicing of the lipoprotein receptor Apoer2. Neuron. 2005;47:567–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
