Ischemia and reperfusion--from mechanism to translation
- PMID: 22064429
- PMCID: PMC3886192
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2507
Ischemia and reperfusion--from mechanism to translation
Abstract
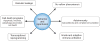
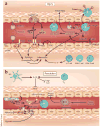
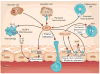
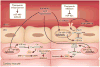
Ischemia and reperfusion-elicited tissue injury contributes to morbidity and mortality in a wide range of pathologies, including myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, acute kidney injury, trauma, circulatory arrest, sickle cell disease and sleep apnea. Ischemia-reperfusion injury is also a major challenge during organ transplantation and cardiothoracic, vascular and general surgery. An imbalance in metabolic supply and demand within the ischemic organ results in profound tissue hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. Subsequent reperfusion further enhances the activation of innate and adaptive immune responses and cell death programs. Recent advances in understanding the molecular and immunological consequences of ischemia and reperfusion may lead to innovative therapeutic strategies for treating patients with ischemia and reperfusion-associated tissue inflammation and organ dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning: a novel protective method from ischemia reperfusion injury--a review.J Surg Res. 2008 Dec;150(2):304-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.12.747. Epub 2008 Jan 22. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 19040966 Review.
-
Liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Pathophysiology and new horizons in preconditioning and therapy.Acta Cir Bras. 2018 Aug;33(8):723-735. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020180080000008. Acta Cir Bras. 2018. PMID: 30208134 Review.
-
[Endothelium function in ischemia-reperfusion (a literature review)].Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2000 Feb;86(2):148-63. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2000. PMID: 10808506 Review. Russian.
-
Hypoxia-induced extracellular vesicles mediate protection of remote ischemic preconditioning for renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;90:473-478. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.096. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28391169
-
RIPC for multiorgan salvage in clinical settings: evolution of concept, evidences and mechanisms.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan 5;746:317-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.08.016. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25176179
Cited by
-
GBT1118, a Voxelotor Analog, Ameliorates Hepatopathy in Sickle Cell Disease.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Sep 26;60(10):1581. doi: 10.3390/medicina60101581. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39459368 Free PMC article.
-
Fingolimod protects against neurovascular unit injury in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Apr;18(4):869-874. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.353500. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36204856 Free PMC article.
-
Immuno-inflammatory pathogenesis in ischemic heart disease: perception and knowledge for neutrophil recruitment.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1411301. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1411301. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39050842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of Tripartite Motif 8 Protects H9C2 Cells Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Injury Through the Activation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720949247. doi: 10.1177/0963689720949247. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32841049 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Aspects of Volatile Anesthetic-Induced Organ Protection and Its Potential in Kidney Transplantation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 8;22(5):2727. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052727. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

