Neuronal activity regulates glutamate transporter dynamics in developing astrocytes
- PMID: 22052455
- PMCID: PMC3232333
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.21249
Neuronal activity regulates glutamate transporter dynamics in developing astrocytes
Abstract
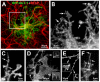
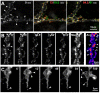
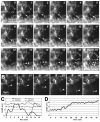
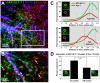
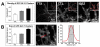
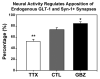
Glutamate transporters (GluTs) maintain a low ambient level of glutamate in the central nervous system (CNS) and shape the activation of glutamate receptors at synapses. Nevertheless, the mechanisms that regulate the trafficking and localization of transporters near sites of glutamate release are poorly understood. Here, we examined the subcellular distribution and dynamic remodeling of the predominant GluT GLT-1 (excitatory amino acid transporter 2, EAAT2) in developing hippocampal astrocytes. Immunolabeling revealed that endogenous GLT-1 is concentrated into discrete clusters along branches of developing astrocytes that were apposed preferentially to synapsin-1 positive synapses. Green fluorescent protein (GFP)-GLT-1 fusion proteins expressed in astrocytes also formed distinct clusters that lined the edges of astrocyte processes, as well as the tips of filopodia and spine-like structures. Time-lapse three-dimensional confocal imaging in tissue slices revealed that GFP-GLT-1 clusters were dynamically remodeled on a timescale of minutes. Some transporter clusters moved within developing astrocyte branches as filopodia extended and retracted, while others maintained stable positions at the tips of spine-like structures. Blockade of neuronal activity with tetrodotoxin reduced both the density and perisynaptic localization of GLT-1 clusters. Conversely, enhancement of neuronal activity increased the size of GLT-1 clusters and their proximity to synapses. Together, these findings indicate that neuronal activity influences both the organization of GluTs in developing astrocyte membranes and their position relative to synapses.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Dec 15;161:107559. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30851309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal activity mediated regulation of glutamate transporter GLT-1 surface diffusion in rat astrocytes in dissociated and slice cultures.Glia. 2016 Jul;64(7):1252-64. doi: 10.1002/glia.22997. Glia. 2016. PMID: 27189737 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal activity and glutamate uptake decrease mitochondrial mobility in astrocytes and position mitochondria near glutamate transporters.J Neurosci. 2014 Jan 29;34(5):1613-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3510-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24478345 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of Astrocytic and Neuronal GLT-1 at Cortical Excitatory Synapses, as Revealed by its Colocalization With Na+/K+-ATPase α Isoforms.Cereb Cortex. 2019 Jul 22;29(8):3331-3350. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhy203. Cereb Cortex. 2019. PMID: 30260367
-
GLT-1: The elusive presynaptic glutamate transporter.Neurochem Int. 2016 Sep;98:19-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27129805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Estimating the glutamate transporter surface density in distinct sub-cellular compartments of mouse hippocampal astrocytes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Feb 4;18(2):e1009845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009845. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35120128 Free PMC article.
-
Appearance of fast astrocytic component in voltage-sensitive dye imaging of neural activity.Mol Brain. 2015 Jun 5;8:35. doi: 10.1186/s13041-015-0127-9. Mol Brain. 2015. PMID: 26043770 Free PMC article.
-
Acute death of astrocytes in blast-exposed rat organotypic hippocampal slice cultures.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 6;12(3):e0173167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173167. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28264063 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1) as a Novel Regulator of Early Astroglial Differentiation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Feb 18;15:642521. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.642521. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33679332 Free PMC article.
-
The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Dec 15;161:107559. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30851309 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez VA, Sabatini BL. Anatomical and physiological plasticity of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:79–97. - PubMed
-
- Benediktsson AM, Schachtele SJ, Green SH, Dailey ME. Ballistic labeling and dynamic imaging of astrocytes in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurosci Methods. 2005;141:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Bergles DE, Jahr CE. Synaptic activation of glutamate transporters in hippocampal astrocytes. Neuron. 1997;19:1297–1308. - PubMed
-
- Buchs P-A, Stoppini L, Muller D. Structural modifications associated with synaptic development in area CA1 of rat hippocampal organotypic cultures. Dev. Brain Res. 1993;71:81–91. - PubMed
-
- Bushong EA, Martone ME, Ellisman MH. Maturation of astrocyte morphology and the establishment of astrocyte domains during postnatal hippocampal development. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2004;22:73–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

