The C terminus of talin links integrins to cell cycle progression
- PMID: 22042621
- PMCID: PMC3206343
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201104128
The C terminus of talin links integrins to cell cycle progression
Abstract
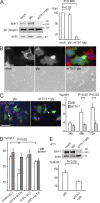
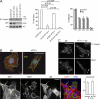
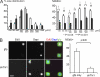
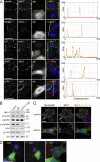
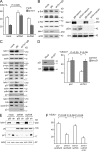
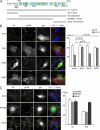
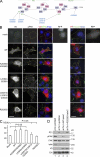
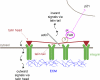
Integrins are cell adhesion receptors that sense the extracellular matrix (ECM) environment. One of their functions is to regulate cell fate decisions, although the question of how integrins initiate intracellular signaling is not fully resolved. In this paper, we examine the role of talin, an adapter protein at cell-matrix attachment sites, in outside-in signaling. We used lentiviral small hairpin ribonucleic acid to deplete talin in mammary epithelial cells. These cells still attached to the ECM in an integrin-dependent manner and spread. They had a normal actin cytoskeleton, but vinculin, paxillin, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), and integrin-linked kinase were not recruited to adhesion sites. Talin-deficient cells showed proliferation defects, and reexpressing a tail portion of the talin rod, but not its head domain, restored integrin-mediated FAK phosphorylation, suppressed p21 expression, and rescued cell cycle. Thus, talin recruits and activates focal adhesion proteins required for proliferation via the C terminus of its rod domain. Our study reveals a new function for talin, which is to link integrin adhesions with cell cycle progression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mapping in vivo associations of cytoplasmic proteins with integrin beta 1 cytoplasmic domain mutants.Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Feb;6(2):151-60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.2.151. Mol Biol Cell. 1995. PMID: 7540435 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin adhesions: who's on first? What's on second? Connections between FAK and talin.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Jul-Aug;6(4):302-6. doi: 10.4161/cam.20488. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22983197 Free PMC article.
-
Talin requires beta-integrin, but not vinculin, for its assembly into focal adhesion-like structures in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Aug;7(8):1181-93. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.8.1181. Mol Biol Cell. 1996. PMID: 8856663 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of talin-dependent integrin signaling and crosstalk.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1838(2):579-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.07.017. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23891718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin signalling at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2009 Jan 15;122(Pt 2):159-63. doi: 10.1242/jcs.018093. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19118207 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Foetal bovine serum-derived exosomes affect yield and phenotype of human cardiac progenitor cell culture.Bioimpacts. 2016;6(1):15-24. doi: 10.15171/bi.2016.03. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Bioimpacts. 2016. PMID: 27340620 Free PMC article.
-
High Plasma Levels of Soluble Talin-1 in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease.Dis Markers. 2020 May 29;2020:2479830. doi: 10.1155/2020/2479830. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 32566035 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative mechanisms for talin to mediate integrin function.Curr Biol. 2015 Mar 30;25(7):847-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.01.043. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 25754646 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of miR-330-5p is associated with carotid plaque's stability by targeting Talin-1 in symptomatic carotid stenosis patients.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019 Jun 18;19(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-1120-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019. PMID: 31215474 Free PMC article.
-
Force-Induced Calpain Cleavage of Talin Is Critical for Growth, Adhesion Development, and Rigidity Sensing.Nano Lett. 2017 Dec 13;17(12):7242-7251. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b02476. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Nano Lett. 2017. PMID: 29052994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barsukov I.L., Prescot A., Bate N., Patel B., Floyd D.N., Bhanji N., Bagshaw C.R., Letinic K., Di Paolo G., De Camilli P., et al. 2003. Phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase type 1gamma and beta1-integrin cytoplasmic domain bind to the same region in the talin FERM domain. J. Biol. Chem. 278:31202–31209 10.1074/jbc.M303850200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cabodi S., Tinnirello A., Di Stefano P., Bisarò B., Ambrosino E., Castellano I., Sapino A., Arisio R., Cavallo F., Forni G., et al. 2006. p130Cas as a new regulator of mammary epithelial cell proliferation, survival, and HER2-neu oncogene-dependent breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 66:4672–4680 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2909 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

