cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)α protein induces interleukin 17A expression and mediates epigenetic alterations at the interleukin-17A gene locus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 22025620
- PMCID: PMC3234851
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.299313
cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)α protein induces interleukin 17A expression and mediates epigenetic alterations at the interleukin-17A gene locus in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
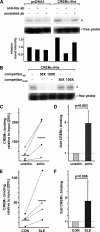
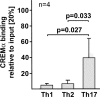
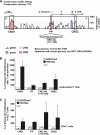
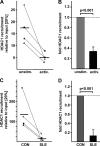
IL-17A is a proinflammatory cytokine that is produced by specialized T helper cells and contributes to the development of several autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Transcription factor cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)α displays increased expression levels in T cells from SLE patients and has been described to account for aberrant T cell function in SLE pathogenesis. In this report, we provide evidence that CREMα physically binds to a cAMP-responsive element, CRE (-111/-104), within the proximal human IL17A promoter and increases its activity. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays reveal that activated naïve CD4(+) T cells as well as T cells from SLE patients display increased CREMα binding to this site compared with T cells from healthy controls. The histone H3 modification pattern at the CRE site (-111/-104) and neighboring conserved noncoding sequences within the human IL17A gene locus suggests an accessible chromatin structure (H3K27 hypomethylation/H3K18 hyperacetylation) in activated naïve CD4(+) T cells and SLE T cells. H3K27 hypomethylation is accompanied by decreased cytosine phosphate guanosine (CpG)-DNA methylation in these regions in SLE T cells. Decreased recruitment of histone deacetylase (HDAC)1 and DNA methyltransferase (DNMT)3a to the CRE site (-111/-104) probably accounts for the observed epigenetic alterations. Reporter studies confirmed that DNA methylation of the IL17A promoter indeed abrogates its inducibility. Our findings demonstrate an extended role for CREMα in the immunopathogenesis of SLE because it contributes to increased expression of IL-17A.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased Set1 binding at the promoter induces aberrant epigenetic alterations and up-regulates cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate response element modulator alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Nov 24;8:126. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0294-2. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27904655 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM)α protein signaling mediates epigenetic remodeling of the human interleukin-2 gene: implications in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 16;286(50):43429-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.299339. Epub 2011 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21976679 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-responsive element modulator α (CREMα) suppresses IL-17F protein expression in T lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 10;287(7):4715-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.323261. Epub 2011 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22184122 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
cAMP responsive element modulator: a critical regulator of cytokine production.Trends Mol Med. 2013 Apr;19(4):262-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Trends Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23491535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cAMP responsive element modulator α promotes effector T cells in systemic autoimmune diseases.Immunology. 2023 Dec;170(4):470-482. doi: 10.1111/imm.13680. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Immunology. 2023. PMID: 37435993 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Dysregulation in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 13;25(2):1019. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021019. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular adenosine induces hypersecretion of IL-17A by T-helper 17 cells through the adenosine A2a receptor.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022 Oct 28;26:100544. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100544. eCollection 2022 Dec. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022. PMID: 36467126 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase 2A enables expression of interleukin 17 (IL-17) through chromatin remodeling.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 13;288(37):26775-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.483743. Epub 2013 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23918926 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Autophagy: A Path to the Control of Autoimmunity.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 14;9:1864. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01864. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30154791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Set1 binding at the promoter induces aberrant epigenetic alterations and up-regulates cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate response element modulator alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Nov 24;8:126. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0294-2. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27904655 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

