Genome-wide identification of microRNA targets in human ES cells reveals a role for miR-302 in modulating BMP response
- PMID: 22012620
- PMCID: PMC3205587
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.17221311
Genome-wide identification of microRNA targets in human ES cells reveals a role for miR-302 in modulating BMP response
Abstract
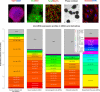
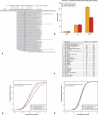
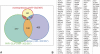
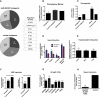
MicroRNAs are important regulators in many cellular processes, including stem cell self-renewal. Recent studies demonstrated their function as pluripotency factors with the capacity for somatic cell reprogramming. However, their role in human embryonic stem (ES) cells (hESCs) remains poorly understood, partially due to the lack of genome-wide strategies to identify their targets. Here, we performed comprehensive microRNA profiling in hESCs and in purified neural and mesenchymal derivatives. Using a combination of AGO cross-linking and microRNA perturbation experiments, together with computational prediction, we identified the targets of the miR-302/367 cluster, the most abundant microRNAs in hESCs. Functional studies identified novel roles of miR-302/367 in maintaining pluripotency and regulating hESC differentiation. We show that in addition to its role in TGF-β signaling, miR-302/367 promotes bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling by targeting BMP inhibitors TOB2, DAZAP2, and SLAIN1. This study broadens our understanding of microRNA function in hESCs and is a valuable resource for future studies in this area.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-135b is a direct PAX6 target and specifies human neuroectoderm by inhibiting TGF-β/BMP signaling.EMBO J. 2014 Jun 2;33(11):1271-83. doi: 10.1002/embj.201387215. Epub 2014 May 6. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 24802670 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding role of miR-302-367 in pluripotency and reprogramming.Cell Cycle. 2012 Apr 15;11(8):1517-23. doi: 10.4161/cc.19846. Epub 2012 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22436490
-
Epigenetic regulation of miR-302 by JMJD1C inhibits neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 24;289(4):2384-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.535799. Epub 2013 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24318875 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β Family Signaling in Embryonic and Somatic Stem-Cell Renewal and Differentiation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 Jul 5;9(7):a022186. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022186. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017. PMID: 28108485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta superfamily in mouse embryonic stem cell self-renewal.Vitam Horm. 2011;87:341-65. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386015-6.00035-4. Vitam Horm. 2011. PMID: 22127250 Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA induced transdifferentiation.F1000 Biol Rep. 2012;4:3. doi: 10.3410/B4-3. Epub 2012 Feb 1. F1000 Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22312415 Free PMC article.
-
The Computational Analysis Conducted on miRNA Target Sites in Association with SNPs at 3'UTR of ADHD-implicated Genes.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(1):58-75. doi: 10.2174/1871524919666191014104843. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31660846 Free PMC article.
-
Pluripotency-Associated microRNAs in Early Vertebrate Embryos and Stem Cells.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 12;14(7):1434. doi: 10.3390/genes14071434. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a pan-cancer oncogenic microRNA superfamily anchored by a central core seed motif.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2730. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3730. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24220575 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated p53 Activities Restrict Differentiation Potential of MicroRNA-Deficient Pluripotent Stem Cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2017 Nov 14;9(5):1604-1617. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.10.006. Stem Cell Reports. 2017. PMID: 29141234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong L, Hughes O, Yung S, Hyslop L, Stewart R, Wappler I, Peters H, Walter T, Stojkovic P, Evans J, et al. 2006. The role of PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK and NFκβ signalling in the maintenance of human embryonic stem cell pluripotency and viability highlighted by transcriptional profiling and functional analysis. Hum Mol Genet 15: 1894–1913 - PubMed
-
- Barberi T, Bradbury M, Dincer Z, Panagiotakos G, Socci ND, Studer L 2007. Derivation of engraftable skeletal myoblasts from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Med 13: 642–648 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
