Stress puts TIA on TOP
- PMID: 22012617
- PMCID: PMC3205582
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.17838411
Stress puts TIA on TOP
Abstract
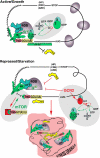
Under conditions of limited nutrients, eukaryotic cells reprogram protein expression in a way that slows growth but enhances survival. Recent data implicate stress granules, discrete cytoplasmic foci into which untranslated mRNPs are assembled during stress, in this process. In the October 1, 2011, issue of Genes & Development, Damgaard and Lykke-Andersen (p. 2057-2068) provide mechanistic insights into the regulation of a specific subset of mRNAs bearing 5'-terminal oligopyrimidine tracts (5'TOPs) by the structurally related stress granule proteins TIA-1 and TIAR.
Figures
Comment on
-
Translational coregulation of 5'TOP mRNAs by TIA-1 and TIAR.Genes Dev. 2011 Oct 1;25(19):2057-68. doi: 10.1101/gad.17355911. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21979918 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Translational coregulation of 5'TOP mRNAs by TIA-1 and TIAR.Genes Dev. 2011 Oct 1;25(19):2057-68. doi: 10.1101/gad.17355911. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21979918 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the cardiomyocyte transcriptome vs translatome by endothelin-1 and insulin: translational regulation of 5' terminal oligopyrimidine tract (TOP) mRNAs by insulin.BMC Genomics. 2010 May 29;11:343. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-343. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20509958 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogenic and nutritional signals are transduced into translational efficiency of TOP mRNAs.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:477-84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2001.66.477. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001. PMID: 12762050 Review. No abstract available.
-
All translation elongation factors and the e, f, and h subunits of translation initiation factor 3 are encoded by 5'-terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNAs.RNA. 2008 Sep;14(9):1730-6. doi: 10.1261/rna.1037108. Epub 2008 Jul 24. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18658124 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase from TOP mRNAs to cell size.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009;90:109-53. doi: 10.1016/S1877-1173(09)90003-5. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009. PMID: 20374740 Review.
Cited by
-
A liaison between mTOR signaling, ribosome biogenesis and cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1849(7):812-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25735853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress Granules and Processing Bodies in Translational Control.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 May 1;11(5):a032813. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032813. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 30082464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DDX6 regulates sequestered nuclear CUG-expanded DMPK-mRNA in dystrophia myotonica type 1.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(11):7186-200. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku352. Epub 2014 May 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24792155 Free PMC article.
-
Human nonsense-mediated RNA decay initiates widely by endonucleolysis and targets snoRNA host genes.Genes Dev. 2014 Nov 15;28(22):2498-517. doi: 10.1101/gad.246538.114. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 25403180 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer biology: The director's cut.Nature. 2012 May 2;485(7396):50-1. doi: 10.1038/485050a. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22552093 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
