Computational modeling of interacting VEGF and soluble VEGF receptor concentration gradients
- PMID: 22007175
- PMCID: PMC3185289
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2011.00062
Computational modeling of interacting VEGF and soluble VEGF receptor concentration gradients
Abstract
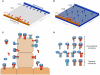
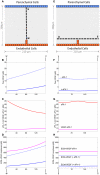
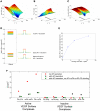
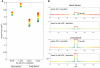
Experimental data indicates that soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 1 (sFlt-1) modulates the guidance cues provided to sprouting blood vessels by VEGF-A. To better delineate the role of sFlt-1 in VEGF signaling, we have developed an experimentally based computational model. This model describes dynamic spatial transport of VEGF, and its binding to receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1, in a mouse embryonic stem cell model of vessel morphogenesis. The model represents the local environment of a single blood vessel. Our simulations predict that blood vessel secretion of sFlt-1 and increased local sFlt-1 sequestration of VEGF results in decreased VEGF-Flk-1 levels on the sprout surface. In addition, the model predicts that sFlt-1 secretion increases the relative gradient of VEGF-Flk-1 along the sprout surface, which could alter endothelial cell perception of directionality cues. We also show that the proximity of neighboring sprouts may alter VEGF gradients, VEGF receptor binding, and the directionality of sprout growth. As sprout distances decrease, the probability that the sprouts will move in divergent directions increases. This model is a useful tool for determining how local sFlt-1 and VEGF gradients contribute to the spatial distribution of VEGF receptor binding, and can be used in conjunction with experimental data to explore how multi-cellular interactions and relationships between local growth factor gradients drive angiogenesis.
Keywords: VEGF; angiogenesis; capillary sprouting; computational model; mathematical model; sFlt-1; vascular development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) coordinates discrete stages of blood vessel formation.Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Jul 1;111(1):84-93. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw091. Epub 2016 May 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2016. PMID: 27142980 Free PMC article.
-
Local guidance of emerging vessel sprouts requires soluble Flt-1.Dev Cell. 2009 Sep;17(3):377-86. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.07.011. Dev Cell. 2009. PMID: 19758562 Free PMC article.
-
The VEGF receptor flt-1 (VEGFR-1) is a positive modulator of vascular sprout formation and branching morphogenesis.Blood. 2004 Jun 15;103(12):4527-35. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-07-2315. Epub 2004 Feb 24. Blood. 2004. PMID: 14982871
-
Spatial-temporal order-disorder transition in angiogenic NOTCH signaling controls cell fate specification.Elife. 2024 Feb 20;12:RP89262. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89262. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38376371 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms in retinal angiogenesis and DiGeorge syndrome.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2005;67(4):229-76. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2005. PMID: 16334858 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular regulation of VEGF: isoforms, proteolysis, and vascular patterning.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Feb;25(1):1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 24332926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) coordinates discrete stages of blood vessel formation.Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Jul 1;111(1):84-93. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw091. Epub 2016 May 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2016. PMID: 27142980 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern formation during vasculogenesis.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2012 Jun;96(2):153-62. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.21010. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2012. PMID: 22692888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood Vessel Patterning on Retinal Astrocytes Requires Endothelial Flt-1 (VEGFR-1).J Dev Biol. 2019 Sep 7;7(3):18. doi: 10.3390/jdb7030018. J Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31500294 Free PMC article.
-
A double-edged sword: the role of VEGF in wound repair and chemoattraction of opportunist pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 30;16(4):7159-72. doi: 10.3390/ijms16047159. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25830483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Autiero M., Waltenberger J., Communi D., Kranz A., Moons L., Lambrechts D., Kroll J., Plaisance S., De Mol M., Bono F., Kliche S., Fellbrich G., Ballmer-Hofer K., Maglione D., Mayr-Beyrle U., Dewerchin M., Dombrowski S., Stanimirovic D., Van Hummelen P., Dehio C., Hicklin D. J., Persico G., Herbert J. M., Communi D., Shibuya M., Collen D., Conway E. M., Carmeliet P. (2003). Role of PlGF in the intra- and intermolecular cross talk between the VEGF receptors Flt1 and Flk1. Nat. Med. 9, 936–94310.1038/nm884 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bautch V.L., Redick S. D., Scalia A., Harmaty M., Carmeliet P., Rapoport R. (2000). Characterization of the vasculogenic block in the absence of vascular endothelial growth factor-A. Blood 95, 1979–1987 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

