Essential PcsB putative peptidoglycan hydrolase interacts with the essential FtsXSpn cell division protein in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39
- PMID: 22006325
- PMCID: PMC3215045
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1108323108
Essential PcsB putative peptidoglycan hydrolase interacts with the essential FtsXSpn cell division protein in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39
Abstract
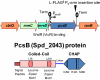
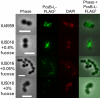
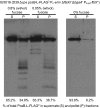
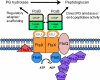
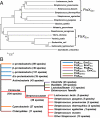
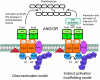
The connection between peptidoglycan remodeling and cell division is poorly understood in ellipsoid-shaped ovococcus bacteria, such as the human respiratory pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. In S. pneumoniae, peptidoglycan homeostasis and stress are regulated by the WalRK (VicRK) two-component regulatory system, which positively regulates expression of the essential PcsB cysteine- and histidine-dependent aminohydrolases/peptidases (CHAP)-domain protein. CHAP-domain proteins usually act as peptidoglycan hydrolases, but purified PcsB lacks detectable enzymatic activity. To explore the functions of PcsB, its subcellular localization was determined. Fractionation experiments showed that cell-bound PcsB was located through hydrophobic interactions on the external membrane surface of pneumococcal cells. Immunofluorescent microscopy localized PcsB mainly to the septa and equators of dividing cells. Chemical cross-linking combined with immunoprecipitation showed that PcsB interacts with the cell division complex formed by membrane-bound FtsX(Spn) and cytoplasmic FtsE(Spn) ATPase, which structurally resemble an ABC transporter. Far Western blotting showed that this interaction was likely through the large extracellular loop of FtsX(Spn) and the amino terminal coiled-coil domain of PcsB. Unlike in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli, we show that FtsX(Spn) and FtsE(Spn) are essential in S. pneumoniae. Consistent with an interaction between PcsB and FtsX(Spn), cells depleted of PcsB or FtsX(Spn) had strikingly similar defects in cell division, and depletion of FtsX(Spn) caused mislocalization of PcsB but not the FtsZ(Spn) early-division protein. A model is presented in which the interaction of the FtsEX(Spn) complex with PcsB activates its peptidoglycan hydrolysis activity and couples peptidoglycan remodeling to pneumococcal cell division.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Biochemical characterization of essential cell division proteins FtsX and FtsE that mediate peptidoglycan hydrolysis by PcsB in Streptococcus pneumoniae.Microbiologyopen. 2016 Oct;5(5):738-752. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.366. Epub 2016 May 10. Microbiologyopen. 2016. PMID: 27167971 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of FtsE ATPase and FtsX extracellular loops 1 and 2 in FtsEX-PcsB complex function in cell division of Streptococcus pneumoniae D39.mBio. 2013 Jul 16;4(4):e00431-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00431-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23860769 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Large Extracellular Loop of FtsX and Its Interaction with the Essential Peptidoglycan Hydrolase PcsB in Streptococcus pneumoniae.mBio. 2019 Jan 29;10(1):e02622-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02622-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30696736 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of FtsEX in cell division.Res Microbiol. 2019 Nov-Dec;170(8):374-380. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Res Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31376483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse paths to midcell: assembly of the bacterial cell division machinery.Curr Biol. 2005 Jul 12;15(13):R514-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.06.038. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16005287 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical characterization of essential cell division proteins FtsX and FtsE that mediate peptidoglycan hydrolysis by PcsB in Streptococcus pneumoniae.Microbiologyopen. 2016 Oct;5(5):738-752. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.366. Epub 2016 May 10. Microbiologyopen. 2016. PMID: 27167971 Free PMC article.
-
FtsEX acts on FtsA to regulate divisome assembly and activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 23;113(34):E5052-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606656113. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27503875 Free PMC article.
-
Two New M23 Peptidoglycan Hydrolases With Distinct Net Charge.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 24;12:719689. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.719689. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34630350 Free PMC article.
-
Metal cofactor stabilization by a partner protein is a widespread strategy employed for amidase activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jun 28;119(26):e2201141119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201141119. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35733252 Free PMC article.
-
Outer membrane barrier impairment by envC deletion reduces gut colonization of Crohn's disease pathobiont Escherichia coli.Microbiology (Reading). 2024 Oct;170(10):001509. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001509. Microbiology (Reading). 2024. PMID: 39405098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henriques-Normark B, Normark S. Commensal pathogens, with a focus on Streptococcus pneumoniae, and interactions with the human host. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316:1408–1414. - PubMed
-
- van der Poll T, Opal SM. Pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia. Lancet. 2009;374:1543–1556. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft EA. Antimicrobial resistance: It's not just for hospitals. JAMA. 2007;298:1803–1804. - PubMed
-
- Black RE, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: A systematic analysis. Lancet. 2010;375:1969–1987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

