A soluble α-synuclein construct forms a dynamic tetramer
- PMID: 22006323
- PMCID: PMC3203798
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1113260108
A soluble α-synuclein construct forms a dynamic tetramer
Abstract
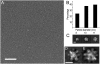
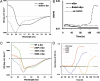
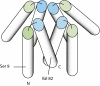
A heterologously expressed form of the human Parkinson disease-associated protein α-synuclein with a 10-residue N-terminal extension is shown to form a stable tetramer in the absence of lipid bilayers or micelles. Sequential NMR assignments, intramonomer nuclear Overhauser effects, and circular dichroism spectra are consistent with transient formation of α-helices in the first 100 N-terminal residues of the 140-residue α-synuclein sequence. Total phosphorus analysis indicates that phospholipids are not associated with the tetramer as isolated, and chemical cross-linking experiments confirm that the tetramer is the highest-order oligomer present at NMR sample concentrations. Image reconstruction from electron micrographs indicates that a symmetric oligomer is present, with three- or fourfold symmetry. Thermal unfolding experiments indicate that a hydrophobic core is present in the tetramer. A dynamic model for the tetramer structure is proposed, based on expected close association of the amphipathic central helices observed in the previously described micelle-associated "hairpin" structure of α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Explaining the structural plasticity of α-synuclein.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Dec 7;133(48):19536-46. doi: 10.1021/ja208657z. Epub 2011 Nov 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 22029383 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic structure of α-synuclein multimers.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Mar 13;135(10):3865-72. doi: 10.1021/ja310518p. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23398399
-
The impact of the E46K mutation on the properties of alpha-synuclein in its monomeric and oligomeric states.Biochemistry. 2007 Jun 19;46(24):7107-18. doi: 10.1021/bi7000246. Epub 2007 May 26. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17530780
-
Preparation and Characterization of Stable α-Synuclein Lipoprotein Particles.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 15;291(16):8516-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.707968. Epub 2016 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26846854 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial in-cell NMR of human α-synuclein: a disordered monomer by nature?Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Oct;40(5):950-4. doi: 10.1042/BST20120096. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22988846 Review.
Cited by
-
From intrinsically disordered protein to context-dependent folding: The α-synuclein tetramer is teased out of hiding.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 4;112(31):9502-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512077112. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26204916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In vivo cross-linking reveals principally oligomeric forms of α-synuclein and β-synuclein in neurons and non-neural cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 1;288(9):6371-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.403311. Epub 2013 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23319586 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of DNA aptamers that prevent the fibrillization of α-synuclein protein in cellular and mouse models.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jun 15;35(3):102251. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102251. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39377064 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational Selection of α-Synuclein Tetramers at Biological Interfaces.J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Oct 28;64(20):8010-8023. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01459. Epub 2024 Oct 8. J Chem Inf Model. 2024. PMID: 39377660 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein oligomers and clinical implications for Parkinson disease.Ann Neurol. 2013 Feb;73(2):155-69. doi: 10.1002/ana.23746. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Ann Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23225525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goedert M. Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:492–501. - PubMed
-
- Jellinger KA. Neuropathological spectrum of synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2003;18(Suppl 6):S2–S12. - PubMed
-
- Klockgether T. Parkinson's disease: Clinical aspects. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;318(1):115–120. - PubMed
-
- George JM, Jin H, Woods WS, Clayton DF. Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron. 1995;15:361–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

