The Ebolavirus VP24 protein blocks phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 21987775
- PMCID: PMC3189987
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jir325
The Ebolavirus VP24 protein blocks phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
Abstract
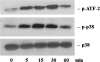
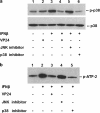
Type I interferon (IFN) signaling is mediated through several signaling pathways, including the Janus kinase and signal transducer and activator (JAK-STAT) and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways. The VP24 protein of Ebolavirus is an IFN antagonist, blocking type I IFN signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway. Here, we show that, in 293 cells, VP24 also interferes with the p38 MAP kinase pathway by blocking IFN-β-stimulated phosphorylation of p38-α. Similar inhibition was not observed in HeLa cells, suggesting cell type-specific differences in signal transduction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase impairs influenza virus-induced primary and secondary host gene responses and protects mice from lethal H5N1 infection.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 3;289(1):13-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.469239. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24189062 Free PMC article.
-
Ebolavirus VP24 binding to karyopherins is required for inhibition of interferon signaling.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(2):1169-75. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01372-09. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19889762 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple anti-apoptotic pathways stimulated by EGF in cytotrophoblasts.Placenta. 2005 Aug;26(7):548-55. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2004.08.012. Placenta. 2005. PMID: 15993704
-
Roles of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the regulation of protein kinase C-alpha activation in interferon-gamma-stimulated macrophages.Immunology. 2009 Sep;128(1 Suppl):e652-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03055.x. Epub 2009 Jan 23. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 19740326 Free PMC article.
-
IKappaB-kinase/nuclear factor-kappaB signaling prevents thermal injury-induced gut damage by inhibiting c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation.Crit Care Med. 2007 May;35(5):1332-40. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000261891.30360.F0. Crit Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17414734
Cited by
-
The multifunctional Ebola virus VP40 matrix protein is a promising therapeutic target.Future Virol. 2015 May;10(5):537-546. doi: 10.2217/fvl.15.6. Future Virol. 2015. PMID: 26120351 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in understanding viral evasion of type I interferon.Immunology. 2013 Mar;138(3):190-7. doi: 10.1111/imm.12038. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23173987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filoviruses: Ecology, Molecular Biology, and Evolution.Adv Virus Res. 2018;100:189-221. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2017.12.002. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Adv Virus Res. 2018. PMID: 29551136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel life cycle modeling system for Ebola virus shows a genome length-dependent role of VP24 in virus infectivity.J Virol. 2014 Sep;88(18):10511-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01272-14. Epub 2014 Jun 25. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24965473 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging targets and novel approaches to Ebola virus prophylaxis and treatment.BioDrugs. 2013 Dec;27(6):565-83. doi: 10.1007/s40259-013-0046-1. BioDrugs. 2013. PMID: 23813435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sen G. Viruses and interferons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55:255–81. - PubMed
-
- Randall R, Goodbourn S. Interferons and viruses: an interplay between induction, signalling, antiviral responses and virus countermeasures. J Gen Virol. 2008;89:1–47. - PubMed
-
- Platanias L. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat Immunol. 2005;5:375–86. - PubMed
-
- Uddin S, Majchrzak B, Woodson J, et al. Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by type interferon. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:30127–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

