Inhibition of PI3K prevents the proliferation and differentiation of human lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts: the role of class I P110 isoforms
- PMID: 21984893
- PMCID: PMC3184941
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024663
Inhibition of PI3K prevents the proliferation and differentiation of human lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts: the role of class I P110 isoforms
Abstract
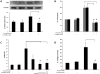
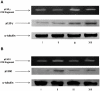
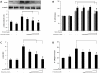
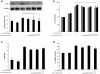
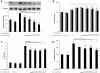
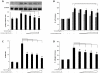
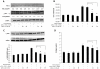
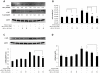
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive fibroproliferative disease characterized by an accumulation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in the alveolar wall. Even though the pathogenesis of this fatal disorder remains unclear, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-induced differentiation and proliferation of myofibroblasts is recognized as a primary event. The molecular pathways involved in TGF-β signalling are generally Smad-dependent yet Smad-independent pathways, including phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt), have been recently proposed. In this research we established ex-vivo cultures of human lung fibroblasts and we investigated the role of the PI3K/Akt pathway in two critical stages of the fibrotic process induced by TGF-β: fibroblast proliferation and differentiation into myofibroblasts. Here we show that the pan-inhibitor of PI3Ks LY294002 is able to abrogate the TGF-β-induced increase in cell proliferation, in α- smooth muscle actin expression and in collagen production besides inhibiting Akt phosphorylation, thus demonstrating the centrality of the PI3K/Akt pathway in lung fibroblast proliferation and differentiation. Moreover, for the first time we show that PI3K p110δ and p110γ are functionally expressed in human lung fibroblasts, in addition to the ubiquitously expressed p110α and β. Finally, results obtained with both selective inhibitors and gene knocking-down experiments demonstrate a major role of p110γ and p110α in both TGF-β-induced fibroblast proliferation and differentiation. This finding suggests that specific PI3K isoforms can be pharmacological targets in IPF.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
PI3K p110γ overexpression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis lung tissue and fibroblast cells: in vitro effects of its inhibition.Lab Invest. 2013 May;93(5):566-76. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.6. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Lab Invest. 2013. PMID: 23439433
-
Resveratrol inhibits transforming growth factor-β-induced proliferation and differentiation of ex vivo human lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts through ERK/Akt inhibition and PTEN restoration.Exp Lung Res. 2011 Apr;37(3):162-74. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2010.524722. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Exp Lung Res. 2011. PMID: 21269063
-
Lipopolysaccharide induces lung fibroblast proliferation through Toll-like receptor 4 signaling and the phosphoinositide3-kinase-Akt pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035926. Epub 2012 Apr 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563417 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan;12(1):18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.023. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35127370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting p110gamma in gastrointestinal cancers: attack on multiple fronts.Front Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;5:391. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00391. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25360116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitor of PD-1/PD-L1: a new approach may be beneficial for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 23;22(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04884-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38263193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXM1 is a critical driver of lung fibroblast activation and fibrogenesis.J Clin Invest. 2018 Jun 1;128(6):2389-2405. doi: 10.1172/JCI87631. Epub 2018 May 7. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29733296 Free PMC article.
-
FoxO3 an important player in fibrogenesis and therapeutic target for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.EMBO Mol Med. 2018 Feb;10(2):276-293. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606261. EMBO Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29217661 Free PMC article.
-
Artemisinin and artemisinin derivatives as anti-fibrotic therapeutics.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Feb;11(2):322-339. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.09.001. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33643815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution of in vitro models of lung fibrosis: promising prospects for drug discovery.Eur Respir Rev. 2024 Jan 17;33(171):230127. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0127-2023. Print 2024 Jan 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2024. PMID: 38232990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(2):277–304. - PubMed
-
- Vancheri C, Failla M, Crimi N, Raghu G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a disease with similarities and links to cancer biology. Eur Respir J. 2010;35:496–504. - PubMed
-
- Coward WR, Saini G, Jenkins G. The pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2010;4(6):367–388. - PubMed
-
- Fine A, Goldstein RH. The effect of transforming growth factor-beta on cell proliferation and collagen formation by lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987;262(8):3897–3902. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Masta S, Meyers D, Narayanan AS. Collagen synthesis by normal and fibrotic human lung fibroblasts and the effect of transforming growth factor-beta. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;140(1):95–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

