Salmonella effector proteins and host-cell responses
- PMID: 21984608
- PMCID: PMC3746315
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-011-0841-0
Salmonella effector proteins and host-cell responses
Abstract
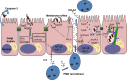
Acute gastroenteritis caused by Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium is a significant public health problem. This pathogen has very sophisticated molecular machinery encoded by the two pathogenicity islands, namely Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 and 2 (SPI-1 and SPI-2). Remarkably, both SPI-1 and SPI-2 are very tightly regulated in terms of timing of expression and spatial localization of the encoded effectors during the infection process within the host cell. This regulation is governed at several levels, including transcription and translation, and by post-translational modifications. In the context of a finely tuned regulatory system, we will highlight how these effector proteins co-opt host signaling pathways that control the ability of the organism to infect and survive within the host, as well as elicit host pro-inflammatory responses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salmonella effectors: important players modulating host cell function during infection.Cell Microbiol. 2011 Dec;13(12):1858-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01701.x. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Cell Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21902796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of Salmonella-Host Cell Interactions through a Dynamic Bacterial Genome.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Sep 29;7:428. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00428. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29034217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of SPI-1 secreted effectors in acute bovine response to Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium: a systems biology analysis approach.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e26869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026869. Epub 2011 Nov 11. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22096503 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of apoptosis by Salmonella pathogenicity island-1 effectors through both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in Salmonella-infected macrophages.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021 Aug;54(4):616-626. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.008. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021. PMID: 32127288
-
Host metabolic shift during systemic Salmonella infection revealed by comparative proteomics.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):1849-1861. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1974316. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 34461813 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A maximum likelihood QTL analysis reveals common genome regions controlling resistance to Salmonella colonization and carrier-state.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 21;13:198. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-198. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22613937 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella Typhimurium expressing chromosomally integrated Schistosoma mansoni Cathepsin B protects against schistosomiasis in mice.NPJ Vaccines. 2023 Feb 27;8(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41541-023-00599-w. NPJ Vaccines. 2023. PMID: 36849453 Free PMC article.
-
A type III effector antagonizes death receptor signalling during bacterial gut infection.Nature. 2013 Sep 12;501(7466):247-51. doi: 10.1038/nature12524. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24025841 Free PMC article.
-
Dormant intracellular Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium discriminates among Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 effectors to persist inside fibroblasts.Infect Immun. 2014 Jan;82(1):221-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01304-13. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24144726 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance: Two-Component Regulatory Systems and Multidrug Efflux Pumps.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 May 26;12(6):965. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12060965. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

