miRNA repression involves GW182-mediated recruitment of CCR4-NOT through conserved W-containing motifs
- PMID: 21984184
- PMCID: PMC3885283
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2166
miRNA repression involves GW182-mediated recruitment of CCR4-NOT through conserved W-containing motifs
Abstract
miRNA-mediated repression in animals is dependent on the GW182 protein family. GW182 proteins are recruited to the miRNA repression complex through direct interaction with Argonaute proteins, and they function downstream to repress target mRNA. Here we demonstrate that in human and Drosophila melanogaster cells, the critical repressive features of both the N-terminal and C-terminal effector domains of GW182 proteins are Gly/Ser/Thr-Trp (G/S/TW) or Trp-Gly/Ser/Thr (WG/S/T) motifs. These motifs, which are dispersed across both domains and act in an additive manner, function by recruiting components of the CCR4-NOT deadenylation complex. A heterologous yeast polypeptide with engineered WG/S/T motifs acquired the ability to repress tethered mRNA and to interact with the CCR4-NOT complex. These results identify previously unknown effector motifs functioning as important mediators of miRNA-induced silencing in both species, and they reveal that recruitment of the CCR4-NOT complex by tryptophan-containing motifs acts downstream of GW182 to repress mRNAs, including inhibiting translation independently of deadenylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

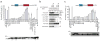
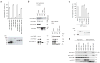

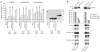
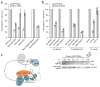
Comment in
-
New insights in the mechanism of microRNA-mediated target repression.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Nov 4;18(11):1181-2. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2170. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22056803 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
miRNA-mediated deadenylation is orchestrated by GW182 through two conserved motifs that interact with CCR4-NOT.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Oct 7;18(11):1211-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2149. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21984185
-
N-terminal Ago-binding domain of GW182 contains a tryptophan-rich region that confer binding to the CCR4-NOT complex.Genes Cells. 2022 Sep;27(9):579-585. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12974. Epub 2022 Jul 24. Genes Cells. 2022. PMID: 35822830
-
The GW/WG repeats of Drosophila GW182 function as effector motifs for miRNA-mediated repression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6673-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq501. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20530530 Free PMC article.
-
The role of GW182 proteins in miRNA-mediated gene silencing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:147-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224969 Review.
-
The GW182 protein family in animal cells: new insights into domains required for miRNA-mediated gene silencing.RNA. 2009 Aug;15(8):1433-42. doi: 10.1261/rna.1703809. Epub 2009 Jun 17. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19535464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Capturing microRNA targets using an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)-trap approach.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 11;109(50):20473-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218887109. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23184980 Free PMC article.
-
Small-RNA loading licenses Argonaute for assembly into a transcriptional silencing complex.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;22(4):328-35. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2979. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25730778 Free PMC article.
-
NOT10 and C2orf29/NOT11 form a conserved module of the CCR4-NOT complex that docks onto the NOT1 N-terminal domain.RNA Biol. 2013 Feb;10(2):228-44. doi: 10.4161/rna.23018. Epub 2013 Jan 9. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23303381 Free PMC article.
-
Early origin and adaptive evolution of the GW182 protein family, the key component of RNA silencing in animals.RNA Biol. 2015;12(7):761-70. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1051302. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26106978 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-mediated mRNA translation activation in quiescent cells and oocytes involves recruitment of a nuclear microRNP.Sci Rep. 2012;2:842. doi: 10.1038/srep00842. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 23150790 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

