Ecdysone- and NO-mediated gene regulation by competing EcR/Usp and E75A nuclear receptors during Drosophila development
- PMID: 21981918
- PMCID: PMC3190167
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.07.033
Ecdysone- and NO-mediated gene regulation by competing EcR/Usp and E75A nuclear receptors during Drosophila development
Abstract
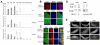
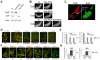
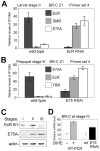
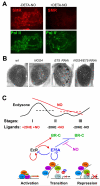
The Drosophila ecdysone receptor (EcR/Usp) is thought to activate or repress gene transcription depending on the presence or absence, respectively, of the hormone ecdysone. Unexpectedly, we found an alternative mechanism at work in salivary glands during the ecdysone-dependent transition from larvae to pupae. In the absense of ecdysone, both ecdysone receptor subunits localize to the cytoplasm, and the heme-binding nuclear receptor E75A replaces EcR/Usp at common target sequences in several genes. During the larval-pupal transition, a switch from gene activation by EcR/Usp to gene repression by E75A is triggered by a decrease in ecdysone concentration and by direct repression of the EcR gene by E75A. Additional control is provided by developmentally timed modulation of E75A activity by NO, which inhibits recruitment of the corepressor SMRTER. These results suggest a mechanism for sequential modulation of gene expression during development by competing nuclear receptors and their effector molecules, ecdysone and NO.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
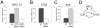

Similar articles
-
rigor mortis encodes a novel nuclear receptor interacting protein required for ecdysone signaling during Drosophila larval development.Development. 2004 Jan;131(1):25-36. doi: 10.1242/dev.00920. Epub 2003 Nov 26. Development. 2004. PMID: 14645129
-
Ecdysone receptor expression and activity in adult Drosophila melanogaster.J Insect Physiol. 2011 Jul;57(7):899-907. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2011.03.027. Epub 2011 Apr 9. J Insect Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21507325
-
Differential control of MHR3 promoter activity by isoforms of the ecdysone receptor and inhibitory effects of E75A and MHR3.Dev Biol. 2004 Aug 15;272(2):510-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.04.028. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15282165
-
Ecdysone signaling in adult Drosophila melanogaster.J Insect Physiol. 2012 Mar;58(3):293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2012.01.013. Epub 2012 Jan 28. J Insect Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22310011 Review.
-
Timing Drosophila development through steroid hormone action.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2024 Feb;84:102148. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2023.102148. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2024. PMID: 38271845 Review.
Cited by
-
Conditional Inhibition of Eip75B Eliminates the Effects of Mating and Mifepristone on Lifespan in Female Drosophila.Cells. 2024 Jun 28;13(13):1123. doi: 10.3390/cells13131123. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994975 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of the ecdysone receptor and its heterodimeric partner ultraspiracle through development in Sciara coprophila.Chromosoma. 2013 Mar;122(1-2):103-19. doi: 10.1007/s00412-012-0395-4. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Chromosoma. 2013. PMID: 23321980 Free PMC article.
-
A fly's view of neuronal remodeling.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2016 Sep;5(5):618-35. doi: 10.1002/wdev.241. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27351747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ecdysone triggered PGRP-LC expression controls Drosophila innate immunity.EMBO J. 2013 May 29;32(11):1626-38. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.100. Epub 2013 May 7. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23652443 Free PMC article.
-
Ecdysone signaling regulates specification of neurons with a male-specific neurite in Drosophila.Biol Open. 2018 Feb 20;7(2):bio029744. doi: 10.1242/bio.029744. Biol Open. 2018. PMID: 29463514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arbeitman MN, Hogness DS. Molecular chaperones activate the Drosophila ecdysone receptor, an RXR heterodimer. Cell. 2000;101:67–77. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M. Ecdysone induction of puffing in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Effects of inhibitors of RNA synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1972;71:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Baker KD, Shewchuk LM, Kozlova T, Makishima M, Hassell A, Wisely B, Caravella JA, Lambert MH, Reinking JL, Krause H, et al. The Drosophila orphan nuclear receptor DHR38 mediates an atypical ecdysteroid signaling pathway. Cell. 2003;113:731–742. - PubMed
-
- Buszczak M, Segraves WA. Insect metamorphosis: out with the old, in with the new. Curr Biol. 2000;10:R830–833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

