Interleukin-36 (IL-36) ligands require processing for full agonist (IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ) or antagonist (IL-36Ra) activity
- PMID: 21965679
- PMCID: PMC3234937
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.267922
Interleukin-36 (IL-36) ligands require processing for full agonist (IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ) or antagonist (IL-36Ra) activity
Abstract
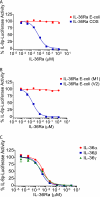
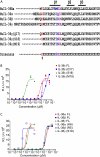
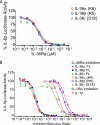
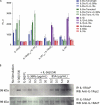
IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ (formerly IL-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9) are IL-1 family members that signal through the IL-1 receptor family members IL-1Rrp2 (IL-1RL2) and IL-1RAcP. IL-36Ra (formerly IL-1F5) has been reported to antagonize IL-36γ. However, our previous attempts to demonstrate IL-36Ra antagonism were unsuccessful. Here, we demonstrate that IL-36Ra antagonist activity is dependent upon removal of its N-terminal methionine. IL-36Ra starting at Val-2 is fully active and capable of inhibiting not only IL-36γ but also IL-36α and IL-36β. Val-2 of IL-36Ra lies 9 amino acids N-terminal to an A-X-Asp motif conserved in all IL-1 family members. In further experiments, we show that truncation of IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ to this same point increased their specific activity by ∼10(3)-10(4)-fold (from EC(50) 1 μg/ml to EC(50) 1 ng/ml). Inhibition of truncated IL-36β activity required ∼10(2)-10(3)-fold excess IL-36Ra, similar to the ratio required for IL-1Ra to inhibit IL-1β. Chimeric receptor experiments demonstrated that the extracellular (but not cytoplasmic) domain of IL-1Rrp2 or IL-1R1 is required for inhibition by their respective natural antagonists. IL-36Ra bound to IL-1Rrp2, and pretreatment of IL-1Rrp2-expressing cells with IL-36Ra prevented IL-36β-mediated co-immunoprecipitation of IL-1Rrp2 with IL-1RAcP. Taken together, these results suggest that the mechanism of IL-36Ra antagonism is analogous to that of IL-1Ra, such that IL-36Ra binds to IL-1Rrp2 and prevents IL-1RAcP recruitment and the formation of a functional signaling complex. In addition, truncation of IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ dramatically enhances their activity, suggesting that post-translational processing is required for full activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of IL-36 cytokines in folliculitis and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.Australas J Dermatol. 2020 Feb;61(1):e39-e45. doi: 10.1111/ajd.13143. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Australas J Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31424098
-
IL-36R ligands are potent regulators of dendritic and T cells.Blood. 2011 Nov 24;118(22):5813-23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-05-356873. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21860022
-
Interleukin (IL)-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 signal through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP to activate the pathway leading to NF-kappaB and MAPKs.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 2;279(14):13677-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400117200. Epub 2004 Jan 20. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14734551
-
The interleukin (IL)-1 cytokine family--Balance between agonists and antagonists in inflammatory diseases.Cytokine. 2015 Nov;76(1):25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.06.017. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26185894 Review.
-
Biology of IL-36 cytokines and their role in disease.Semin Immunol. 2013 Dec 15;25(6):458-65. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Semin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24355486 Review.
Cited by
-
The IL-23/T17 pathogenic axis in psoriasis is amplified by keratinocyte responses.Trends Immunol. 2013 Apr;34(4):174-81. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2012.11.005. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Trends Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23291100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-1 Family Antagonists in Mouse and Human Skin Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 16;12:652846. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.652846. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33796114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Autoinflammatory psoriasis"-genetics and biology of pustular psoriasis.Cell Mol Immunol. 2021 Feb;18(2):307-317. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0519-3. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32814870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-36 Cytokine/Receptor Signaling: A New Target for Tissue Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6458. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186458. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting IL-36 in Inflammatory Skin Diseases.BioDrugs. 2023 May;37(3):279-293. doi: 10.1007/s40259-023-00587-5. Epub 2023 Mar 3. BioDrugs. 2023. PMID: 36867370
References
-
- Dunn E., Sims J. E., Nicklin M. J., O'Neill L. A. (2001) Trends Immunol. 22, 533–536 - PubMed
-
- Sims J. E., Smith D. E. (2010) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10, 89–102 - PubMed
-
- O'Neill L. A. (2008) Immunol. Rev. 226, 10–18 - PubMed
-
- Greenfeder S. A., Nunes P., Kwee L., Labow M., Chizzonite R. A., Ju G. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13757–13765 - PubMed
-
- Born T. L., Thomassen E., Bird T. A., Sims J. E. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 29445–29450 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

