Creating highly specific nucleases by fusion of active restriction endonucleases and catalytically inactive homing endonucleases
- PMID: 21965534
- PMCID: PMC3258161
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr788
Creating highly specific nucleases by fusion of active restriction endonucleases and catalytically inactive homing endonucleases
Abstract
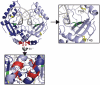
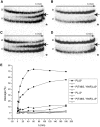
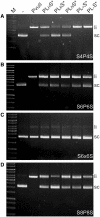
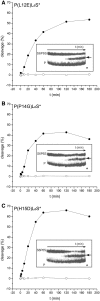
Zinc-finger nucleases and TALE nucleases are produced by combining a specific DNA-binding module and a non-specific DNA-cleavage module, resulting in nucleases able to cleave DNA at a unique sequence. Here a new approach for creating highly specific nucleases was pursued by fusing a catalytically inactive variant of the homing endonuclease I-SceI, as DNA binding-module, to the type IIP restriction enzyme PvuII, as cleavage module. The fusion enzymes were designed to recognize a composite site comprising the recognition site of PvuII flanked by the recognition site of I-SceI. In order to reduce activity on PvuII sites lacking the flanking I-SceI sites, the enzymes were optimized so that the binding of I-SceI to its sites positions PvuII for cleavage of the composite site. This was achieved by optimization of the linker and by introducing amino acid substitutions in PvuII which decrease its activity or disturb its dimer interface. The most specific variant showed a more than 1000-fold preference for the addressed composite site over an unaddressed PvuII site. These results indicate that using a specific restriction enzyme, such as PvuII, as cleavage module, offers an alternative to the otherwise often used catalytic domain of FokI, which by itself does not contribute to the specificity of the engineered nuclease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Site- and strand-specific nicking of DNA by fusion proteins derived from MutH and I-SceI or TALE repeats.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr;41(7):e83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt080. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23408850 Free PMC article.
-
A novel zinc-finger nuclease platform with a sequence-specific cleavage module.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(6):2623-38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1112. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22135304 Free PMC article.
-
TALE-PvuII fusion proteins--novel tools for gene targeting.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 5;8(12):e82539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082539. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349308 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and engineered nicking endonucleases--from cleavage mechanism to engineering of strand-specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(1):1-18. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq742. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20805246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel site-specific DNA endonucleases.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998 Feb;8(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(98)80005-5. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998. PMID: 9519292 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA cleavage enzymes for treatment of persistent viral infections: recent advances and the pathway forward.Virology. 2014 Apr;454-455:353-61. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.12.037. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24485787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compact designer TALENs for efficient genome engineering.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1762. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2782. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23612303 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Alternative Nucleases in the Age of CRISPR/Cas9.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 29;18(12):2565. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122565. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29186020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site- and strand-specific nicking of DNA by fusion proteins derived from MutH and I-SceI or TALE repeats.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr;41(7):e83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt080. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23408850 Free PMC article.
-
The monomeric GIY-YIG homing endonuclease I-BmoI uses a molecular anchor and a flexible tether to sequentially nick DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 May 1;41(10):5413-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt186. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23558745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pingoud A, Wende W. Generation of novel nucleases with extended specificity by rational and combinatorial strategies. ChemBioChem. 2011;12:1495–1500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

