Nuclear retention of importin α coordinates cell fate through changes in gene expression
- PMID: 21964068
- PMCID: PMC3252573
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.360
Nuclear retention of importin α coordinates cell fate through changes in gene expression
Abstract
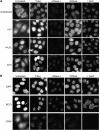
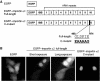
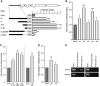
Various cellular stresses including oxidative stress induce a collapse of the Ran gradient, which causes accumulation of importin α in the nucleus and a subsequent block of nuclear protein import. However, it is unknown whether accumulated importin α performs roles in the nucleus after its migration in response to stress. In this study, we found that nuclear-retained importin α2 binds with DNase I-sensitive nuclear component(s) and exhibits selective upregulation of mRNA encoding Serine/threonine kinase 35 (STK35) by microarray analysis. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and promoter analysis demonstrated that importin α2 can access to the promoter region of STK35 and accelerate its transcription in response to hydrogen peroxide exposure. Furthermore, constitutive overexpression of STK35 proteins enhances caspase-independent cell death under oxidative stress conditions. These results collectively reveal that nuclear-localized importin α2 influences gene expression and contributes directly to cell fate outcomes including non-apoptotic cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
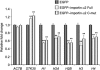
Similar articles
-
Cellular stresses induce the nuclear accumulation of importin alpha and cause a conventional nuclear import block.J Cell Biol. 2004 Jun 7;165(5):617-23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200312008. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15184398 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear importin α and its physiological importance.Commun Integr Biol. 2012 Mar 1;5(2):220-2. doi: 10.4161/cib.19194. Commun Integr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22808339 Free PMC article.
-
Importin-beta mediates Cdc7 nuclear import by binding to the kinase insert II domain, which can be antagonized by importin-alpha.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 28;281(17):12041-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512630200. Epub 2006 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16492669
-
Importin-alpha protein binding to a nuclear localization signal of carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP).J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 12;286(32):28119-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.237016. Epub 2011 Jun 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21665952 Free PMC article.
-
Importin α: a key molecule in nuclear transport and non-transport functions.J Biochem. 2016 Aug;160(2):69-75. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvw036. Epub 2016 Jun 11. J Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27289017 Review.
Cited by
-
Coronary artery disease: differential expression of ceRNAs and interaction analyses.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Feb;9(3):229. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3487. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33708856 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress mediates nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of KPNA2 via AKT1-CDK1 axis-regulated S62 phosphorylation.FASEB Bioadv. 2024 Jul 5;6(8):276-288. doi: 10.1096/fba.2024-00078. eCollection 2024 Aug. FASEB Bioadv. 2024. PMID: 39114447 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane association of importin α facilitates viral entry into salivary gland cells of vector insects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jul 27;118(30):e2103393118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2103393118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34290144 Free PMC article.
-
Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation: Quantitative Analysis of In Cell Interaction of Nuclear Transporter Importin α with Cargo Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2502:215-233. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2337-4_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35412241
-
An Analysis Regarding the Prognostic Significance of MAVS and Its Underlying Biological Mechanism in Ovarian Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 14;9:728061. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.728061. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34722508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, Sali A, Rout MP (2007) The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature 450: 695–701 - PubMed
-
- Chan CK, Jans DA (1999) Synergy of importin α recognition and DNA binding by the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. FEBS Lett 462: 221–224 - PubMed
-
- Eguchi Y, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y (1997) Intracellular ATP levels determine cell death fate by apoptosis or necrosis. Cancer Res 57: 1835–1840 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

