RNA-binding protein HuR autoregulates its expression by promoting alternative polyadenylation site usage
- PMID: 21948791
- PMCID: PMC3258158
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr783
RNA-binding protein HuR autoregulates its expression by promoting alternative polyadenylation site usage
Abstract
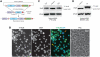
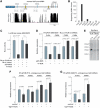
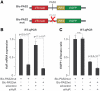
RNA-binding protein HuR modulates the stability and translational efficiency of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) encoding essential components of the cellular proliferation, growth and survival pathways. Consistent with these functions, HuR levels are often elevated in cancer cells and reduced in senescent and quiescent cells. However, the molecular mechanisms that control HuR expression are poorly understood. Here we show that HuR protein autoregulates its abundance through a negative feedback loop that involves interaction of the nuclear HuR protein with a GU-rich element (GRE) overlapping with the HuR major polyadenylation signal (PAS2). An increase in the cellular HuR protein levels stimulates the expression of long HuR mRNA species containing an AU-rich element (ARE) that destabilizes the mRNAs and thus reduces the protein production output. The PAS2 read-through occurs due to a reduced recruitment of the CstF-64 subunit of the pre-mRNA cleavage stimulation factor in the presence of the GRE-bound HuR. We propose that this mechanism maintains HuR homeostasis in proliferating cells. Since only the nuclear HuR is expected to contribute to the auto-regulation, our model may explain the longstanding observation that the increase in the total HuR expression in cancer cells often correlates with the accumulation of its substantial fraction in the cytoplasm.
Figures

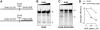
Similar articles
-
Neuron-specific ELAV/Hu proteins suppress HuR mRNA during neuronal differentiation by alternative polyadenylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(6):2734-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1114. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22139917 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative polyadenylation variants of the RNA binding protein, HuR: abundance, role of AU-rich elements and auto-Regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jun;37(11):3612-24. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp223. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19359363 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of ERBB2 by miR26a/b and HuR confers resistance to tamoxifen in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 18;292(33):13551-13564. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.780973. Epub 2017 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28637868 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the mRNA-binding protein HuR by posttranslational modification: spotlight on phosphorylation.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Jun;13(4):380-90. doi: 10.2174/138920312801619439. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22708484 Review.
-
Alternative polyadenylation of mRNA precursors.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jan;18(1):18-30. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.116. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27677860 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The RNA-binding protein RNPC1 stabilizes the mRNA encoding the RNA-binding protein HuR and cooperates with HuR to suppress cell proliferation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 27;287(18):14535-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.326827. Epub 2012 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22371495 Free PMC article.
-
Neuron-specific ELAV/Hu proteins suppress HuR mRNA during neuronal differentiation by alternative polyadenylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(6):2734-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1114. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22139917 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon regulatory factor 1 and a variant of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L coordinately silence the gene for adhesion protein CEACAM1.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 15;293(24):9277-9291. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001507. Epub 2018 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29720400 Free PMC article.
-
Compensatory expression regulation of highly homologous proteins HNRNPA1 and HNRNPA2.Turk J Biol. 2021 Apr 20;45(2):187-195. doi: 10.3906/biy-2010-29. eCollection 2021. Turk J Biol. 2021. PMID: 33907500 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Postoperative Ileus by Lentivirus-Mediated HuR RNA Interference via the p38/MK2 Signaling Pathway.J Gastrointest Surg. 2017 Feb;21(2):389-397. doi: 10.1007/s11605-016-3303-z. Epub 2016 Oct 27. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017. PMID: 27796636
References
-
- Moore MJ. From birth to death: the complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science. 2005;309:1514–1518. - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ, Proudfoot NJ. Pre-mRNA processing reaches back to transcription and ahead to translation. Cell. 2009;136:688–700. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez-Diaz P, Penalva LO. Post-transcription meets post-genomic: the saga of RNA binding proteins in a new era. RNA Biol. 2006;3:101–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

