The dual role of sirtuins in cancer
- PMID: 21941620
- PMCID: PMC3174263
- DOI: 10.1177/1947601911417862
The dual role of sirtuins in cancer
Abstract
Among the greatest challenges facing organisms is that of detecting and effectively responding to life-threatening environmental changes that are intimately associated with metabolic fluctuations and certain forms of stress. These conditions have been linked to the onset of many human pathologies, including cancer. Over the past decade, members of the Sir2 family, or sirtuins, have been described as major players in sensing and coordinating stress response. Evidence has imputed mammalian sirtuins in carcinogenesis, although the mechanisms involved seem to be more diverse and complex than previously anticipated. Some sirtuins, such as SirT2 and SirT6, seem to work as tumor suppressors, but others, such as SirT1, are apparently bifunctional: operating as both tumor suppressors and oncogenic factors depending on the context and the study conditions. The mechanisms underlying these apparently contradictory activities are not well understood, although recent findings suggest that they might actually be two sides of the same coin. In this review, the authors summarize current knowledge on the functional implications of sirtuins in cancer and discuss possible explanations for their functional duality.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA repair; SirT1-7; cancer; deacetylation; genome stability; heterochromatin; sirtuins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
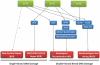
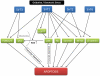


Similar articles
-
Sirtuins and SIRT6 in Carcinogenesis and in Diet.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 7;20(19):4945. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194945. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31591350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuins and Type 2 Diabetes: Role in Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Function.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Mar 27;10:187. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00187. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30972029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current understanding and future perspectives of the roles of sirtuins in the reprogramming and differentiation of pluripotent stem cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Mar;243(6):563-575. doi: 10.1177/1535370218759636. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 29557214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of sirtuins on tumorigenesis: possible link between aging and cancer.BMB Rep. 2013 Sep;46(9):429-38. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.9.180. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 24064057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuins in gamete biology and reproductive physiology: emerging roles and therapeutic potential in female and male infertility.Hum Reprod Update. 2018 May 1;24(3):267-289. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmy003. Hum Reprod Update. 2018. PMID: 29447380 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting mutant p53 by a SIRT1 activator YK-3-237 inhibits the proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2013 Jul;4(7):984-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1070. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 23846322 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation of ELF5 suppresses breast cancer progression by promoting its degradation and targeting CCND1.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021 Mar 19;5(1):20. doi: 10.1038/s41698-021-00158-3. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33742100 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 6 Is a Critical Epigenetic Regulator of Cancer.Subcell Biochem. 2022;100:337-360. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-07634-3_10. Subcell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36301499 Review.
-
A small molecule Inauhzin inhibits SIRT1 activity and suppresses tumour growth through activation of p53.EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Apr;4(4):298-312. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100211. Epub 2012 Feb 13. EMBO Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22331558 Free PMC article.
-
BZD9L1 sirtuin inhibitor as a potential adjuvant for sensitization of colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2019 Sep 27;11:1758835919878977. doi: 10.1177/1758835919878977. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31632470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sinclair DA, Guarente L. Extrachromosomal rDNA circles—a cause of aging in yeast. Cell. 1997;91:1033-42 - PubMed
-
- Saunders LR, Verdin E. Sirtuins: critical regulators at the crossroads between cancer and aging. Oncogene. 2007;26:5489-504 - PubMed
-
- Guarente L. Diverse and dynamic functions of the Sir silencing complex. Nat Genet. 1999;23:281-5 - PubMed
-
- Braunstein M, Rose AB, Holmes SG, Allis CD, Broach JR. Transcriptional silencing in yeast is associated with reduced nucleosome acetylation. Genes Dev. 1993;7:592-604 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
