ST6Gal-I regulates macrophage apoptosis via α2-6 sialylation of the TNFR1 death receptor
- PMID: 21930713
- PMCID: PMC3234788
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.276063
ST6Gal-I regulates macrophage apoptosis via α2-6 sialylation of the TNFR1 death receptor
Abstract
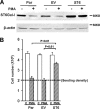
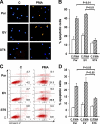
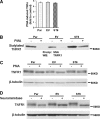
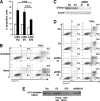
Macrophages play a central role in innate immunity, however mechanisms regulating macrophage survival are not fully understood. Herein we describe a novel apoptotic pathway involving α2-6 sialylation of the TNFR1 death receptor by the ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase. Variant glycosylation of TNFR1 has not previously been implicated in TNFR1 function, and little is known regarding the TNFR1 glycan composition. To study sialylation in macrophages, we treated U937 monocytic cells with PMA, which stimulates both macrophage differentiation and apoptosis. Interestingly, macrophage differentiation induces ST6Gal-I down-regulation, leading to reduced α2-6 sialylation of selected receptors. To prevent loss of α2-6 sialylation, we forced constitutive expression of ST6Gal-I, and found that this strongly inhibited PMA-induced apoptosis. Given that PMA-mediated apoptosis is thought to result from up-regulation of TNFα, which then activates TNFR1, we next evaluated the α2-6 sialylation of TNFR1. U937 cells with forced ST6Gal-I displayed TNFR1 with elevated α2-6 sialylation, and this was associated with diminished TNFα-stimulated apoptosis. Correspondingly, removal of α2-6 sialylation from TNFR1 through either neuraminidase treatment or expression of ST6Gal-I shRNA markedly enhanced TNFα-mediated apoptosis. To confirm the physiologic importance of TNFR1 sialylation, we generated overexpressing ST6Gal-I transgenic mice. Peritoneal macrophages from transgenic lines displayed TNFR1 with elevated α2-6 sialylation, and these cells were significantly protected against TNFα-stimulated apoptosis. Moreover, greater numbers of thioglycollate-induced peritoneal cells were observed in transgenic mice. These collective results highlight a new mechanism of TNFR1 regulation, and further intimate that loss of α2-6 sialylation during macrophage differentiation may limit macrophage lifespan by sensitizing cells to TNFα-stimulated apoptosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated cancer cell survival via sialylation of the TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) death receptor.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 2;293(5):1610-1622. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.801480. Epub 2017 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29233887 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of α2,6-sialylation mediates the invasiveness and tumorigenicity of non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo via Notch1/Hes1/MMPs pathway.Int J Cancer. 2018 Nov 1;143(9):2319-2330. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31737. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29981167
-
Sialylation of the Fas death receptor by ST6Gal-I provides protection against Fas-mediated apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 1;286(26):22982-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.211375. Epub 2011 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21550977 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of β-Galactoside α2,6 Sialyltranferase 1 in Cancers.Molecules. 2015 Apr 24;20(5):7509-27. doi: 10.3390/molecules20057509. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25919275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phylogenetic-Derived Insights into the Evolution of Sialylation in Eukaryotes: Comprehensive Analysis of Vertebrate β-Galactoside α2,3/6-Sialyltransferases (ST3Gal and ST6Gal).Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 9;17(8):1286. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081286. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27517905 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ST6Gal-I protein expression is upregulated in human epithelial tumors and correlates with stem cell markers in normal tissues and colon cancer cell lines.Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 1;73(7):2368-78. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3424. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23358684 Free PMC article.
-
Sialylation of N-glycans: mechanism, cellular compartmentalization and function.Histochem Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;147(2):149-174. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1520-x. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27975143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ST6Gal1: Oncogenic signaling pathways and targets.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Aug 29;9:962908. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.962908. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36106023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Glycans on Key Cell Surface Receptors That Regulate Cell Proliferation and Cell Death.Cells. 2021 May 19;10(5):1252. doi: 10.3390/cells10051252. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34069424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Tumor-Associated Glycosyltransferase ST6Gal-I Regulates Stem Cell Transcription Factors and Confers a Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype.Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 1;76(13):3978-88. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2834. Epub 2016 May 23. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27216178 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

