Assemblathon 1: a competitive assessment of de novo short read assembly methods
- PMID: 21926179
- PMCID: PMC3227110
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.126599.111
Assemblathon 1: a competitive assessment of de novo short read assembly methods
Abstract
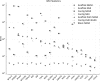
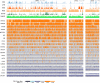
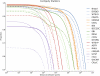
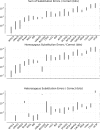
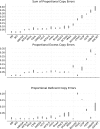
Low-cost short read sequencing technology has revolutionized genomics, though it is only just becoming practical for the high-quality de novo assembly of a novel large genome. We describe the Assemblathon 1 competition, which aimed to comprehensively assess the state of the art in de novo assembly methods when applied to current sequencing technologies. In a collaborative effort, teams were asked to assemble a simulated Illumina HiSeq data set of an unknown, simulated diploid genome. A total of 41 assemblies from 17 different groups were received. Novel haplotype aware assessments of coverage, contiguity, structure, base calling, and copy number were made. We establish that within this benchmark: (1) It is possible to assemble the genome to a high level of coverage and accuracy, and that (2) large differences exist between the assemblies, suggesting room for further improvements in current methods. The simulated benchmark, including the correct answer, the assemblies, and the code that was used to evaluate the assemblies is now public and freely available from http://www.assemblathon.org/.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Benchmarking of de novo assembly algorithms for Nanopore data reveals optimal performance of OLC approaches.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 22;17 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):507. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2895-8. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27556636 Free PMC article.
-
High-quality draft assemblies of mammalian genomes from massively parallel sequence data.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 25;108(4):1513-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017351108. Epub 2010 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21187386 Free PMC article.
-
Completion of draft bacterial genomes by long-read sequencing of synthetic genomic pools.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jul 29;21(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06910-6. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32727443 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation and the de novo assembly of human genomes.Nat Rev Genet. 2015 Nov;16(11):627-40. doi: 10.1038/nrg3933. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Nat Rev Genet. 2015. PMID: 26442640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome-level hybrid de novo genome assemblies as an attainable option for nonmodel insects.Mol Ecol Resour. 2020 Sep;20(5):1277-1293. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13176. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Mol Ecol Resour. 2020. PMID: 32329220 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a previously undescribed divergent virus from the Flaviviridae family in an outbreak of equine serum hepatitis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 9;110(15):E1407-15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219217110. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23509292 Free PMC article.
-
Tips and tricks for the assembly of a Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis genome using a semiconductor sequencer.Microb Biotechnol. 2013 Mar;6(2):150-6. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12006. Epub 2012 Dec 2. Microb Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23199210 Free PMC article.
-
QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies.Bioinformatics. 2013 Apr 15;29(8):1072-5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23422339 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and classifying trait linked polymorphisms in non-reference species by walking coloured de bruijn graphs.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60058. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060058. Epub 2013 Mar 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23536903 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstructing mitochondrial genomes directly from genomic next-generation sequencing reads--a baiting and iterative mapping approach.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jul;41(13):e129. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt371. Epub 2013 May 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23661685 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- F31 HG000064/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003474/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U41HG004568/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004695/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U24CA143858-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG004568/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 HG000064/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P41HG002371/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG004555/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 HG002371/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG00064/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA022707/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004695/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG004555/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
