Ethanol-induced increase in Fyn kinase activity in the dorsomedial striatum is associated with subcellular redistribution of protein tyrosine phosphatase α
- PMID: 21919909
- PMCID: PMC3205081
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07485.x
Ethanol-induced increase in Fyn kinase activity in the dorsomedial striatum is associated with subcellular redistribution of protein tyrosine phosphatase α
Abstract
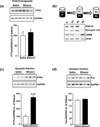
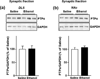
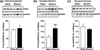
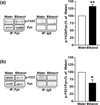
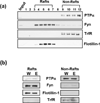
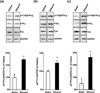
In vivo exposure of rodents to ethanol leads to a long-lasting increase in Fyn kinase activity in the dorsomedial striatum (DMS). In this study, we set out to identify a molecular mechanism that contributes to the enhancement of Fyn activity in response to ethanol in the DMS. Protein tyrosine phosphatase α (PTPα) positively regulates the activity of Fyn, and we found that repeated systemic administration or binge drinking of ethanol results in an increase in the synaptic localization of PTPα in the DMS, the same site where Fyn resides. We also demonstrate that binge drinking of ethanol leads to an increase in Fyn activity and to the co-localization of Fyn and PTPα in lipid rafts in the DMS. Finally, we show that the level of tyrosine phosphorylated (and thus active) PTPα in the synaptic fractions is increased in response to contingent or non-contingent exposure of rats to ethanol. Together, our results suggest that the redistribution of PTPα in the DMS into compartments where Fyn resides is a potential mechanism by which the activity of the kinase is increased upon ethanol exposure. Such neuroadaptations could be part of a mechanism that leads to the development of excessive ethanol consumption.
© 2011 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2011 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of the manuscript have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethanol-mediated facilitation of AMPA receptor function in the dorsomedial striatum: implications for alcohol drinking behavior.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 24;32(43):15124-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2783-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23100433 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase α in the dorsomedial striatum promotes excessive ethanol-drinking behaviors.J Neurosci. 2013 Sep 4;33(36):14369-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1954-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24005290 Free PMC article.
-
Striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase regulates the PTPα/Fyn signaling pathway.J Neurochem. 2015 Aug;134(4):629-41. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13160. Epub 2015 May 25. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25951993 Free PMC article.
-
Long-lasting adaptations of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the dorsomedial striatum play a crucial role in alcohol consumption and relapse.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 28;30(30):10187-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2268-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20668202 Free PMC article.
-
Striatal involvement in human alcoholism and alcohol consumption, and withdrawal in animal models.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Oct;35(10):1739-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01520.x. Epub 2011 May 25. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21615425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Neurotrophic Factor Receptor p75 in the Rat Dorsolateral Striatum Drives Excessive Alcohol Drinking.J Neurosci. 2016 Sep 28;36(39):10116-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4597-14.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 28. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27683907 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol-mediated facilitation of AMPA receptor function in the dorsomedial striatum: implications for alcohol drinking behavior.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 24;32(43):15124-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2783-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23100433 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-Fyn signaling in the dorsomedial striatum direct pathway drives excessive alcohol use.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021 Jan;46(2):334-342. doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0712-1. Epub 2020 May 17. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 32417851 Free PMC article.
-
The Fyn kinase inhibitor, AZD0530, suppresses mouse alcohol self-administration and seeking.Addict Biol. 2019 Nov;24(6):1227-1234. doi: 10.1111/adb.12699. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Addict Biol. 2019. PMID: 30536923 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin accessibility mapping of the striatum identifies tyrosine kinase FYN as a therapeutic target for heroin use disorder.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 14;11(1):4634. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18114-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32929078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe T, Matsumura S, Katano T, et al. Fyn kinase-mediated phosphorylation of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit at Tyr1472 is essential for maintenance of neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;22:1445–1454. - PubMed
-
- Allen JA, Halverson-Tamboli RA, Rasenick MM. Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:128–140. - PubMed
-
- Besshoh S, Bawa D, Teves L, Wallace MC, Gurd JW. Increased phosphorylation and redistribution of NMDA receptors between synaptic lipid rafts and post-synaptic densities following transient global ischemia in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 2005;93:186–194. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari V, Lim KL, Pallen CJ. Physical and functional interactions between receptor-like protein-tyrosine phosphatase alpha and p59fyn. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:8691–8698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

