The biogenesis and characterization of mammalian microRNAs of mirtron origin
- PMID: 21914725
- PMCID: PMC3245937
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr722
The biogenesis and characterization of mammalian microRNAs of mirtron origin
Abstract
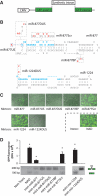
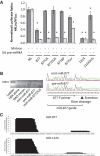
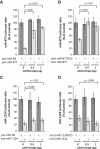
Mirtrons, short hairpin pre-microRNA (miRNA) mimics directly produced by intronic splicing, have recently been identified and experimentally confirmed in invertebrates. While there is evidence to suggest several mammalian miRNAs have mirtron origins, this has yet to be experimentally demonstrated. Here, we characterize the biogenesis of mammalian mirtrons by ectopic expression of splicing-dependent mirtron precursors. The putative mirtrons hsa-miR-877, hsa-miR-1226 and mmu-miR-1224 were designed as introns within eGFP. Correct splicing and function of these sequences as introns was shown through eGFP fluorescence and RT-PCR, while all mirtrons suppressed perfectly complementary luciferase reporter targets to levels similar to that of corresponding independently expressed pre-miRNA controls. Splicing-deficient mutants and disruption of key steps in miRNA biogenesis demonstrated that mirtron-mediated gene knockdown was splicing-dependent, Drosha-independent and had variable dependence on RNAi pathway elements following pre-miRNA formation. The silencing effect of hsa-miR-877 was further demonstrated to be mediated by the generation of short anti-sense RNA species expressed with low abundance. Finally, the mammalian mirtron hsa-miR-877 was shown to reduce mRNA levels of an endogenous transcript containing hsa-miR-877 target sites in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells. This work confirms the mirtron origins of three mammalian miRNAs and suggests that they are a functional class of splicing-dependent miRNAs which are physiologically active.
Figures
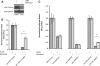
Similar articles
-
Intronic microRNA precursors that bypass Drosha processing.Nature. 2007 Jul 5;448(7149):83-6. doi: 10.1038/nature05983. Epub 2007 Jun 24. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17589500 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Alternative Splicing Sites on Mirtron Formation and Arm Selection of Precursor microRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 12;25(14):7643. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147643. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062888 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing-dependent expression of microRNAs of mirtron origin in human digestive and excretory system cancer cells.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Mar 25;8:33. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0200-y. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27019673 Free PMC article.
-
Mirtrons: microRNA biogenesis via splicing.Biochimie. 2011 Nov;93(11):1897-904. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.06.017. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21712066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis, characterization, and functions of mirtrons.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022 Jan;13(1):e1680. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1680. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022. PMID: 34155810 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of miRNA biogenesis as an integrated component of growth factor signaling.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Apr;25(2):233-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.12.005. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23312066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tensor GSVD of patient- and platform-matched tumor and normal DNA copy-number profiles uncovers chromosome arm-wide patterns of tumor-exclusive platform-consistent alterations encoding for cell transformation and predicting ovarian cancer survival.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 15;10(4):e0121396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121396. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25875127 Free PMC article.
-
Human mirtrons can express functional microRNAs simultaneously from both arms in a flanking exon-independent manner.RNA Biol. 2012 Sep;9(9):1177-85. doi: 10.4161/rna.21359. Epub 2012 Sep 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 23018783 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs that associate with YB-1 alter proliferation in prostate cancer cells.RNA. 2015 Jun;21(6):1159-72. doi: 10.1261/rna.045559.114. Epub 2015 Apr 22. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25904138 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of hundreds of mirtrons in mouse and human small RNA data.Genome Res. 2012 Sep;22(9):1634-45. doi: 10.1101/gr.133553.111. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22955976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, Nam JW, Heo I, Rhee JK, Sohn SY, Cho Y, Zhang BT, Kim VN. Molecular basis for the recognition of primary microRNAs by the Drosha-DGCR8 complex. Cell. 2006;125:887–901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

