Sex differences in resident immune cell phenotype underlie more efficient acute inflammatory responses in female mice
- PMID: 21911834
- PMCID: PMC5363818
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-340281
Sex differences in resident immune cell phenotype underlie more efficient acute inflammatory responses in female mice
Abstract
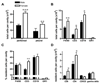
Females are protected against mortality arising from severe sepsis; however, the precise mechanisms that confer this survival advantage in females over males are unclear. Resident leukocytes in resting tissues have a significant influence on circulating cytokine levels and recruitment of blood leukocytes during acute inflammatory responses. Whether the phenotype of resident leukocytes is distinct in females is unknown. In the present study, we show that the numbers of leukocytes occupying the naive peritoneal and pleural cavities is higher in female than in male mice and rats, comprising more T and B lymphocytes and macrophages. The altered immune cell composition of the female peritoneum is controlled by elevated tissue chemokine expression. Female resident macrophages also exhibit greater TLR expression and enhanced phagocytosis and NADPH oxidase-mediated bacterial killing. However, macrophage-derived cytokine production is diminished by proportionally more resident immunomodulatory CD4+ T lymphocytes. Ovarian hormones regulate macrophage phenotype, function, and numbers, but have no significant impact on T-lymphocyte populations in females. We have identified a fundamental sex difference in phenotype of resident leukocytes. We propose that the distinct resident leukocyte population in females allows aggressive recognition and elimination of diverse infectious stimuli without recruitment of circulating neutrophils or excessive cytokine production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicting financial interests.
Figures
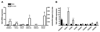
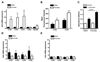
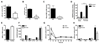
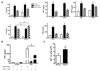
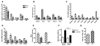
Comment in
-
Go girls! Efficient female innate immunity.Blood. 2011 Nov 24;118(22):5718-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-381137. Blood. 2011. PMID: 22123906 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
LSP1 modulates leukocyte populations in resting and inflamed peritoneum.Blood. 2000 Sep 1;96(5):1827-35. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10961883
-
Resident peritoneal leukocytes are important sources of MMP-9 during zymosan peritonitis: superior contribution of macrophages over mast cells.Immunol Lett. 2007 Nov 15;113(2):99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.07.017. Epub 2007 Aug 24. Immunol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17826846
-
Resident peritoneal macrophages and mast cells are important cellular sites of COX-1 and COX-2 activity during acute peritoneal inflammation.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2009 Nov-Dec;57(6):459-66. doi: 10.1007/s00005-009-0053-6. Epub 2009 Nov 3. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2009. PMID: 19885646
-
Induction of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 in murine resident peritoneal macrophages by monosodium urate monohydrate crystals.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Feb;54(2):455-62. doi: 10.1002/art.21633. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16447220
-
Shades of white: new insights into tissue-resident leukocyte heterogeneity.FEBS J. 2022 Jan;289(2):308-318. doi: 10.1111/febs.15737. Epub 2021 Feb 16. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 33513286 Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-species comparison of airway epithelium transcriptomics.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 22;10(19):e38259. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38259. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39391497 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Aberrant Neutrophil Trafficking and Subsequent Remote Lung Injury.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(38):e2400647. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400647. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39119837 Free PMC article.
-
Role of sex as a biological variable in neonatal alveolar macrophages.Redox Biol. 2024 Sep;75:103296. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103296. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 39098263 Free PMC article.
-
A New Application for Cenicriviroc, a Dual CCR2/CCR5 Antagonist, in the Treatment of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in a Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 5;25(13):7410. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137410. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000516 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-183/96/182 cluster regulates sensory innervation, resident myeloid cells and functions of the cornea through cell type-specific target genes.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 1;14(1):7676. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58403-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38561433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adrie C, Azoulay E, Francais A, et al. Influence of gender on the outcome of severe sepsis: a reappraisal. Chest. 2007;132:1786–1793. - PubMed
-
- Marriott I, Huet-Hudson YM. Sexual dimorphism in innate immune responses to infectious organisms. Immunol Res. 2006;34(3):177–92. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Cook NR, Lee I-M, et al. A randomized trial of low-dose aspirin in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(13):1293–304. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg H, Allard D. Evidence for caution: Women and statin use. Women and Health Protection Report. 2007 Jun
-
- Straub RH. The complex role of estrogens in inflammation. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:521–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

