β-Actin specifically controls cell growth, migration, and the G-actin pool
- PMID: 21900491
- PMCID: PMC3204067
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0582
β-Actin specifically controls cell growth, migration, and the G-actin pool
Abstract
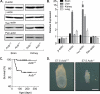
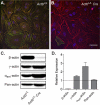
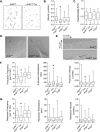
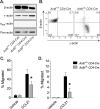
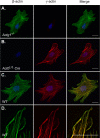
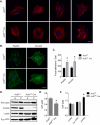
Ubiquitously expressed β-actin and γ-actin isoforms play critical roles in most cellular processes; however, their unique contributions are not well understood. We generated whole-body β-actin-knockout (Actb(-/-)) mice and demonstrated that β-actin is required for early embryonic development. Lethality of Actb(-/-) embryos correlated with severe growth impairment and migration defects in β-actin-knockout primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) that were not observed in γ-actin-null MEFs. Migration defects were associated with reduced membrane protrusion dynamics and increased focal adhesions. We also identified migration defects upon conditional ablation of β-actin in highly motile T cells. Of great interest, ablation of β-actin altered the ratio of globular actin (G-actin) to filamentous actin in MEFs, with corresponding changes in expression of genes that regulate the cell cycle and motility. These data support an essential role for β-actin in regulating cell migration and gene expression through control of the cellular G-actin pool.
Figures
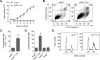
Similar articles
-
Cells lacking β-actin are genetically reprogrammed and maintain conditional migratory capacity.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Aug;11(8):255-71. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.015099. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22448045 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of ACTB and ACTG1 with CRISPR/Cas9(D10A) Technique Shows that Non-Muscle β and γ Actin Are Not Equal in Relation to Human Melanoma Cells' Motility and Focal Adhesion Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2746. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082746. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326615 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed embryonic development and impaired cell growth and survival in Actg1 null mice.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010 Sep;67(9):564-72. doi: 10.1002/cm.20467. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010. PMID: 20662086 Free PMC article.
-
Time for rethinking the different β-actin transgenic mouse models?Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020 Dec;77(12):527-543. doi: 10.1002/cm.21647. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 33249765 Review.
-
Actin isoform expression patterns during mammalian development and in pathology: insights from mouse models.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Oct;66(10):798-815. doi: 10.1002/cm.20350. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009. PMID: 19296487 Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity from similarity: cellular strategies for assigning particular identities to actin filaments and networks.Open Biol. 2020 Sep;10(9):200157. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200157. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32873155 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-directed knockdown in the cnidarian fish blood parasite Sphaerospora molnari.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 12;14(1):3545. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54171-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38347054 Free PMC article.
-
γ-Actin plays a key role in endothelial cell motility and neovessel maintenance.Vasc Cell. 2015 Feb 6;7:2. doi: 10.1186/s13221-014-0027-2. eCollection 2015. Vasc Cell. 2015. PMID: 25705373 Free PMC article.
-
The makings of the 'actin code': regulation of actin's biological function at the amino acid and nucleotide level.J Cell Sci. 2018 May 8;131(9):jcs215509. doi: 10.1242/jcs.215509. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29739859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconsidering an active role for G-actin in cytoskeletal regulation.J Cell Sci. 2018 Jan 10;131(1):jcs203760. doi: 10.1242/jcs.203760. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29321224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dugina V, Zwaenepoel I, Gabbiani G, Clement S, Chaponnier C. Beta and gamma-cytoplasmic actins display distinct distribution and functional diversity. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:2980–2988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

