Overexpression of VEGF189 in breast cancer cells induces apoptosis via NRP1 under stress conditions
- PMID: 21897119
- PMCID: PMC3210301
- DOI: 10.4161/cam.5.4.17287
Overexpression of VEGF189 in breast cancer cells induces apoptosis via NRP1 under stress conditions
Abstract
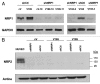
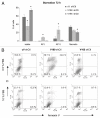
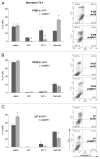
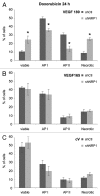
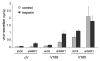
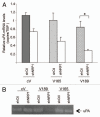
The existence of multiple VEGF-A isoforms raised the possibility that they may have distinct functions in tumor growth. We have previously published that VEGF189 and VEGF165 contribute to breast cancer progression and angiogenesis, but VEGF165 induced the most rapid tumor uptake. Since VEGF165 has been described as a survival factor for breast tumor cells, we questioned here the effects of VEGF189 on the survival/apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells. We used clones which overexpress VEGF189 (V189) or VEGF165 (V165) isoforms and compared them to a control one (cV). Overexpression of VEGF189 resulted in increased cell apoptosis, as determined by Annexin-V apoptosis assay, under serum starvation and doxorubicin treatment, while VEGF 165 was confirmed to be a survival factor. Since MDA-MB-231 highly express NRP1 (a co-receptor for VEGF-A), we used short hairpin RNA (shRNA) to knockdown NRP1 expression. V189shNRP1 clones were characterized by reduced apoptosis and higher necrosis, as compared to V189shCtl, under stress conditions. Unexpectedly, NRP1 knock-down had no effect on the survival or apoptosis of V165 cells. VEGF189 showed greater affinity towards NRP1 than VEGF165 using a BIAcore binding assay. Finally, since endogenously produced urokinase-type plasminogen (uPA) has been found to prevent apoptosis in breast cancers, we analyzed the level of uPA activity in our clones. An inhibition of uPA activity was observed in V189shNRP1 clones. Altogether, these results suggest a major role of NRP1 in apoptosis induced by VEGF189 in stress conditions and confirm VEGF165 as a survival factor.
Figures
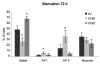
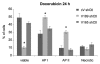
Similar articles
-
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells overexpressing single VEGF isoforms display distinct colonisation characteristics.Br J Cancer. 2015 Sep 1;113(5):773-85. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.267. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26196186 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor 189 in breast cancer cells leads to delayed tumor uptake with dilated intratumoral vessels.Am J Pathol. 2008 Jan;172(1):167-78. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070181. Epub 2007 Dec 13. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18079435 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF189 binds NRP1 and is sufficient for VEGF/NRP1-dependent neuronal patterning in the developing brain.Development. 2015 Jan 15;142(2):314-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.115998. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Development. 2015. PMID: 25519242 Free PMC article.
-
Long isoform of VEGF stimulates cell migration of breast cancer by filopodia formation via NRP1/ARHGAP17/Cdc42 regulatory network.Int J Cancer. 2018 Dec 1;143(11):2905-2918. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31645. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29971782 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of neuropilin-1 by RNA-interference and its angiostatic potential in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Z Gastroenterol. 2010 Jan;48(1):21-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109907. Epub 2010 Jan 13. Z Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20072992
Cited by
-
Shift in VEGFA isoform balance towards more angiogenic variants is associated with tumor stage and differentiation of human hepatocellular carcinoma.PeerJ. 2018 Jun 5;6:e4915. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4915. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 29888133 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-148a functions to suppress metastasis and serves as a prognostic indicator in triple-negative breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 12;7(15):20381-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7953. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26967387 Free PMC article.
-
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells overexpressing single VEGF isoforms display distinct colonisation characteristics.Br J Cancer. 2015 Sep 1;113(5):773-85. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.267. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26196186 Free PMC article.
-
NRP1 function and targeting in neurovascular development and eye disease.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016 May;52:64-83. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2016.02.003. Epub 2016 Feb 27. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26923176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VEGF-A121a binding to Neuropilins - A concept revisited.Cell Adh Migr. 2018 May 4;12(3):204-214. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2017.1372878. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 29095088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tischer E, Mitchell R, Hartman T, Silva M, ospodarowicz D, Fiddes JC, et al. The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor. Multiple protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:11947–11954. - PubMed
-
- Gitay-Goren H, Soker S, Vlodavsky I, Neufeld G. The binding of vascular endothelial growth factor to its receptors is dependent on cell surface-associated heparin-like molecules. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:6093–6098. - PubMed
-
- Houck KA, Leung DW, Rowland AM, Winer J, Ferrara N. Dual regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor bioavailability by genetic and proteolytic mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:26031–26037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
