Germline deletion of the miR-17∼92 cluster causes skeletal and growth defects in humans
- PMID: 21892160
- PMCID: PMC3184212
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.915
Germline deletion of the miR-17∼92 cluster causes skeletal and growth defects in humans
Abstract
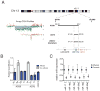
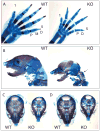
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key regulators of gene expression in animals and plants. Studies in a variety of model organisms show that miRNAs modulate developmental processes. To our knowledge, the only hereditary condition known to be caused by a miRNA is a form of adult-onset non-syndromic deafness, and no miRNA mutation has yet been found to be responsible for any developmental defect in humans. Here we report the identification of germline hemizygous deletions of MIR17HG, encoding the miR-17∼92 polycistronic miRNA cluster, in individuals with microcephaly, short stature and digital abnormalities. We demonstrate that haploinsufficiency of miR-17∼92 is responsible for these developmental abnormalities by showing that mice harboring targeted deletion of the miR-17∼92 cluster phenocopy several key features of the affected humans. These findings identify a regulatory function for miR-17∼92 in growth and skeletal development and represent the first example of an miRNA gene responsible for a syndromic developmental defect in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A de novo 13q31.3 microduplication encompassing the miR-17 ~ 92 cluster results in features mirroring those associated with Feingold syndrome 2.Gene. 2020 Aug 30;753:144816. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144816. Epub 2020 May 27. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32473250
-
De novo 13q31.1-q32.1 interstitial deletion encompassing the miR-17-92 cluster in a patient with Feingold syndrome-2.Am J Med Genet A. 2013 Apr;161A(4):894-6. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35781. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Am J Med Genet A. 2013. PMID: 23495052 No abstract available.
-
An allelic series of miR-17 ∼ 92-mutant mice uncovers functional specialization and cooperation among members of a microRNA polycistron.Nat Genet. 2015 Jul;47(7):766-75. doi: 10.1038/ng.3321. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Nat Genet. 2015. PMID: 26029871 Free PMC article.
-
A fourth case of Feingold syndrome type 2: psychiatric presentation and management.BMJ Case Rep. 2014 Nov 12;2014:bcr2014207501. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-207501. BMJ Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 25391829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic factors in esophageal atresia, tracheo-esophageal fistula and the VACTERL association: roles for FOXF1 and the 16q24.1 FOX transcription factor gene cluster, and review of the literature.Eur J Med Genet. 2010 Jan-Feb;53(1):6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2009.10.001. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Eur J Med Genet. 2010. PMID: 19822228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The developmental miR-17-92 cluster and the Sfmbt2 miRNA cluster cannot rescue the abnormal embryonic development generated using obstructive epididymal environment-producing sperm in C57BL/6 J mice.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022 Nov 30;20(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12958-022-01025-x. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36451157 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in kidney development and disease.JCI Insight. 2022 May 9;7(9):e158277. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.158277. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35531954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR17~92 restrains pro-apoptotic BIM to ensure survival of haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.Cell Death Differ. 2020 May;27(5):1475-1488. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0430-6. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 31591473 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by Long Non-coding RNA.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017 Jun;15(3):177-186. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.12.005. Epub 2017 May 19. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28529100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-17-92 cluster mediates the proliferation and survival of neural progenitor cells after stroke.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 3;288(18):12478-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.449025. Epub 2013 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23511639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mencia A, et al. Mutations in the seed region of human miR-96 are responsible for nonsyndromic progressive hearing loss. Nat Genet. 2009;41:609–13. - PubMed
-
- Hayashita Y, et al. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005;65:9628–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

