In vivo induction of Tr1 cells via mucosal dendritic cells and AHR signaling
- PMID: 21886804
- PMCID: PMC3160310
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023618
In vivo induction of Tr1 cells via mucosal dendritic cells and AHR signaling
Abstract
Background: Type 1 regulatory T (Tr1) cells, characterized by the secretion of high levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10), play an important role in the regulation of autoimmune diseases and transplantation. However, effective strategies that specifically induce Tr1 cells in vivo are limited. Furthermore, the pathways controlling the induction of these cells in vivo are not well understood.
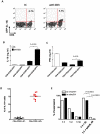
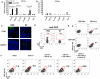
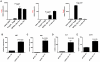
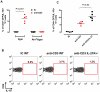
Methodology/principal findings: Here we report that nasal administration of anti-CD3 antibody induces suppressive Tr1 cells in mice. The in vivo induction of Tr1 cells by nasal anti-CD3 is dependent on IL-27 produced by upper airway resident dendritic cells (DCs), and is controlled by the transcription factors aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) and c-Maf. Subsequently, IL-21 acts in an autocrine fashion to expand and maintain the Tr1 cells induced in vivo by nasally administered anti-CD3.
Conclusions/significance: Our findings identify a unique approach to generate Tr1 cells in vivo and provide insights into the mechanisms by which these cells are induced.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cisplatin induces tolerogenic dendritic cells in response to TLR agonists via the abundant production of IL-10, thereby promoting Th2- and Tr1-biased T-cell immunity.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):33765-82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9260. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27172902 Free PMC article.
-
An endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand acts on dendritic cells and T cells to suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 30;107(48):20768-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009201107. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21068375 Free PMC article.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacts with c-Maf to promote the differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells induced by IL-27.Nat Immunol. 2010 Sep;11(9):854-61. doi: 10.1038/ni.1912. Epub 2010 Aug 1. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20676095 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 regulatory T cells (Tr1) in autoimmunity.Semin Immunol. 2011 Jun;23(3):202-8. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2011.07.005. Epub 2011 Aug 12. Semin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21840222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular pathways in the induction of interleukin-27-driven regulatory type 1 cells.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010 Jun;30(6):381-8. doi: 10.1089/jir.2010.0047. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010. PMID: 20540648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: a molecular pathway for the environmental control of the immune response.Immunology. 2013 Mar;138(3):183-9. doi: 10.1111/imm.12046. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23190340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation in Astrocytes by Laquinimod Ameliorates Autoimmune Inflammation in the CNS.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021 Jan 6;8(2):e946. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000946. Print 2021 Mar 4. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021. PMID: 33408169 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Plasma Agonist Activity Correlates With Disease Activity in Progressive MS.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2020 Dec 24;8(2):e933. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000933. Print 2021 Mar. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2020. PMID: 33361385 Free PMC article.
-
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia. An Example of Disrupted Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Mediated Immunological Homeostasis in the Skin?Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020 Jul 27;13:479-484. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S262803. eCollection 2020. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32801823 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor control of adaptive immunity.Pharmacol Rev. 2013 Aug 1;65(4):1148-61. doi: 10.1124/pr.113.007823. Print 2013. Pharmacol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23908379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Groux H, O'Garra A, Bigler M, Rouleau M, Antonenko S, et al. A CD4+ T-cell subset inhibits antigen-specific T-cell responses and prevents colitis. Nature. 1997;389:737–742. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:531–562. - PubMed
-
- Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR, Shi Y, et al. Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:929–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

