Characteristics and outcomes of patients with advanced gastric cancer who declined to participate in a randomized clinical chemotherapy trial
- PMID: 21886493
- PMCID: PMC3092652
- DOI: 10.1200/JOP.2010.000106
Characteristics and outcomes of patients with advanced gastric cancer who declined to participate in a randomized clinical chemotherapy trial
Abstract
Purpose: There is insufficient data to verify whether participation in clinical trials in itself can lead to better clinical outcomes. We have analyzed the characteristics and outcomes of patients who declined to participate in a randomized trial in comparison with those who participated in the trial.
Patients and methods: A randomized trial for naive advanced gastric cancer was offered to 286 patients. The trial investigated the superiority of irinotecan plus cisplatin and the noninferiority of S-1 compared with continuous fluorouracil infusion. We retrospectively reviewed the characteristics and outcomes for both participants and nonparticipants in this trial.
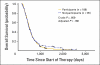
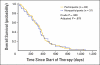
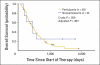
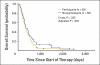
Results: Of the 286 patients, 98 (34%) declined to participate in the trial. The rate of declining was significantly higher among younger patients (P = .003), and it varied significantly between attending physicians (range, 23% to 58%; P = .004). There were no other significant correlations between rate of declining and patient characteristics. No significant differences were observed in the clinical outcomes between the participants and nonparticipants, for whom the median survival times were 367 versus 347 days, respectively. The hazard ratio for overall survival, adjusted for other confounding variables, was 1.21 (95% CI, 0.91 to 1.60). No interaction was observed between participation and the various regimens.
Conclusion: There was no difference in clinical outcomes between participants and nonparticipants. However, the patient's age and the doctor-patient relationship may have an effect on patient accrual to randomized trials.
Figures
Comment in
- J Oncol Pract. 7(3):153.
Similar articles
-
Characteristics and outcomes of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer who declined to participate in randomised clinical chemotherapy trials.Br J Cancer. 2009 Apr 7;100(7):1037-42. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604982. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Br J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19293799 Free PMC article.
-
A study of second-line irinotecan plus cisplatin vs. irinotecan alone in platinum-naïve patients with early relapse of gastric cancer refractory to adjuvant S-1 monotherapy: exploratory subgroup analysis of the randomized phase III TRICS trial.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 May;83(5):867-874. doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03802-9. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30806758 Clinical Trial.
-
Fluorouracil versus combination of irinotecan plus cisplatin versus S-1 in metastatic gastric cancer: a randomised phase 3 study.Lancet Oncol. 2009 Nov;10(11):1063-9. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70259-1. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Lancet Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19818685 Clinical Trial.
-
Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Mar 17;(3):CD004064. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004064.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 29;8:CD004064. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004064.pub4 PMID: 20238327 Updated. Review.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(15):iii-ix, xi-162. doi: 10.3310/hta12150. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462574 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of neoadjuvant trastuzumab and chemotherapy in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013 Jul;139(7):1229-40. doi: 10.1007/s00432-013-1436-y. Epub 2013 Apr 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23604446 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of clinical trial participation on survival in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer: a multi-center analysis.BMC Cancer. 2018 Apr 26;18(1):468. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4390-x. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29695228 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of clinical trial participation versus non-participation on overall survival in men receiving first-line docetaxel-containing chemotherapy for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.BJU Int. 2012 Dec;110(11 Pt B):E575-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11286.x. Epub 2012 Jun 15. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 22702837 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of survival outcomes among cancer patients treated in and out of clinical trials.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014 Mar;106(3):dju002. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju002. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014. PMID: 24627276 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Patients with Newly Diagnosed Transplant-Ineligible Multiple Myeloma According to Clinical Trials Enrollment: Experience of a Single Institution.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;15(21):5261. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215261. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lara PN, Jr, Higdon R, Lim N, et al. Prospective evaluation of cancer clinical trial accrual patterns: Identifying potential barriers to enrolment. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:1728–1733. - PubMed
-
- Go RS, Frisby KA, Lee JA, et al. Clinical trial accrual among new cancer patients at a community-based cancer center. Cancer. 2006;106:426–433. - PubMed
-
- Nott L, Yeend S, Pirc L, et al. Successfully improving access and accrual to oncology clinical trials. Cancer. 2007;109:1451–1453. - PubMed
-
- Umutyan A, Chiechi C, Beckett LA, et al. Overcoming barriers to cancer clinical trial accrual. Cancer. 2008;112:212–219. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

