Aging and amyloid beta-induced oxidative DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: implications for early intervention and therapeutics
- PMID: 21871956
- PMCID: PMC3185172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.08.005
Aging and amyloid beta-induced oxidative DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: implications for early intervention and therapeutics
Abstract
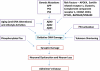
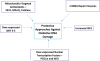
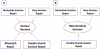
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an age-related progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting thousands of people in the world and effective treatment is still not available. Over two decades of intense research using AD postmortem brains, transgenic mouse and cell models of amyloid precursor protein and tau revealed that amyloid beta (Aβ) and hyperphosphorylated tau are synergistically involved in triggering disease progression. Accumulating evidence also revealed that aging and amyloid beta-induced oxidative DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction initiate and contributes to the development and progression of the disease. The purpose of this article is to summarize the latest progress in aging and AD, with a special emphasis on the mitochondria, oxidative DNA damage including methods of its measurement. It also discusses the therapeutic approaches against oxidative DNA damage and treatment strategies in AD.
2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amyloid beta, mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage: implications for cognitive decline in aging and Alzheimer's disease.Trends Mol Med. 2008 Feb;14(2):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2007.12.002. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Trends Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18218341 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid Beta and Phosphorylated Tau-Induced Defective Autophagy and Mitophagy in Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2019 May 22;8(5):488. doi: 10.3390/cells8050488. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31121890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid-beta and mitochondria in aging and Alzheimer's disease: implications for synaptic damage and cognitive decline.J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S499-512. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-100504. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20413847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defective mitophagy in Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Dec;64:101191. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101191. Epub 2020 Oct 3. Ageing Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 33022416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal tau, mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired axonal transport of mitochondria, and synaptic deprivation in Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res. 2011 Sep 30;1415:136-48. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.07.052. Epub 2011 Jul 31. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21872849 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective effect of low-dose paracetamol treatment against cognitive dysfunction in d-galactose-induced aging mice.Heliyon. 2022 Oct 15;8(10):e11108. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11108. eCollection 2022 Oct. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36281406 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid beta modulators and neuroprotection in Alzheimer's disease: a critical appraisal.Drug Discov Today. 2017 Feb;22(2):223-233. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2016.10.010. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Drug Discov Today. 2017. PMID: 27794478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dye-binding assays for evaluation of the effects of small molecule inhibitors on amyloid (aβ) self-assembly.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012 Nov 21;3(11):807-19. doi: 10.1021/cn300076x. Epub 2012 Aug 6. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23173064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps in central nervous system pathologies: A mini review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 17;10:1083242. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1083242. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36873885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organ reserve, excess metabolic capacity, and aging.Biogerontology. 2018 Apr;19(2):171-184. doi: 10.1007/s10522-018-9746-8. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Biogerontology. 2018. PMID: 29335816 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol.Rev. 2001;81:741–766. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer's Association. Thies W, Bleiler L. 2011 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:208–244. - PubMed
-
- LaFerla FM, Green KN, Oddo S. Intracellular amyloid-beta in Alzheimer's disease. Nat.Rev.Neurosci. 2007;8:499–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

