The inhibitory effect of phospholemman on the sodium pump requires its palmitoylation
- PMID: 21868384
- PMCID: PMC3195638
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.282145
The inhibitory effect of phospholemman on the sodium pump requires its palmitoylation
Abstract
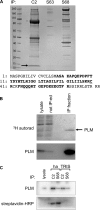
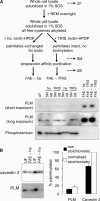
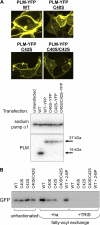
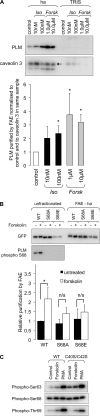
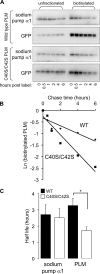
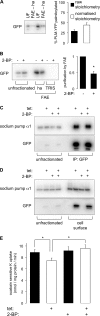
Phospholemman (PLM), the principal sarcolemmal substrate for protein kinases A and C in the heart, regulates the cardiac sodium pump. We investigated post-translational modifications of PLM additional to phosphorylation in adult rat ventricular myocytes (ARVM). LC-MS/MS of tryptically digested PLM immunoprecipitated from ARVM identified cysteine 40 as palmitoylated in some peptides, but no information was obtained regarding the palmitoylation status of cysteine 42. PLM palmitoylation was confirmed by immunoprecipitating PLM from ARVM loaded with [(3)H]palmitic acid and immunoblotting following streptavidin affinity purification from ARVM lysates subjected to fatty acyl biotin exchange. Mutagenesis identified both Cys-40 and Cys-42 of PLM as palmitoylated. Phosphorylation of PLM at serine 68 by PKA in ARVM or transiently transfected HEK cells increased its palmitoylation, but PKA activation did not increase the palmitoylation of S68A PLM-YFP in HEK cells. Wild type and unpalmitoylatable PLM-YFP were all correctly targeted to the cell surface membrane, but the half-life of unpalmitoylatable PLM was reduced compared with wild type. In cells stably expressing inducible PLM, PLM expression inhibited the sodium pump, but PLM did not inhibit the sodium pump when palmitoylation was inhibited. Hence, palmitoylation of PLM controls its turnover, and palmitoylated PLM inhibits the sodium pump. Surprisingly, phosphorylation of PLM enhances its palmitoylation, probably through the enhanced mobility of the phosphorylated intracellular domain increasing the accessibility of cysteines for the palmitoylating enzyme, with interesting theoretical implications. All FXYD proteins have conserved intracellular cysteines, so FXYD protein palmitoylation may be a universal means to regulate the sodium pump.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Substrate recognition by the cell surface palmitoyl transferase DHHC5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 9;111(49):17534-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1413627111. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25422474 Free PMC article.
-
A separate pool of cardiac phospholemman that does not regulate or associate with the sodium pump: multimers of phospholemman in ventricular muscle.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13808-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.460956. Epub 2013 Mar 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23532852 Free PMC article.
-
Greasing the wheels or a spanner in the works? Regulation of the cardiac sodium pump by palmitoylation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Apr;53(2):175-191. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2018.1432560. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29424237 Review.
-
Nitric oxide regulates cardiac intracellular Na⁺ and Ca²⁺ by modulating Na/K ATPase via PKCε and phospholemman-dependent mechanism.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Aug;61:164-71. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.04.013. Epub 2013 Apr 20. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23612119 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated regulation of cardiac Na(+)/Ca (2+) exchanger and Na (+)-K (+)-ATPase by phospholemman (FXYD1).Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:175-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224879 Review.
Cited by
-
DHHC5 Mediates β-Adrenergic Signaling in Cardiomyocytes by Targeting Gα Proteins.Biophys J. 2020 Feb 25;118(4):826-835. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.08.018. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 31547976 Free PMC article.
-
Control of protein palmitoylation by regulating substrate recruitment to a zDHHC-protein acyltransferase.Commun Biol. 2020 Jul 31;3(1):411. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01145-3. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32737405 Free PMC article.
-
Control of cardiac contraction by sodium: Promises, reckonings, and new beginnings.Cell Calcium. 2020 Jan;85:102129. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102129. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Cell Calcium. 2020. PMID: 31835176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substrate recognition by the cell surface palmitoyl transferase DHHC5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 9;111(49):17534-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1413627111. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25422474 Free PMC article.
-
Na/K pump regulation of cardiac repolarization: insights from a systems biology approach.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Feb;466(2):183-93. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1293-1. Epub 2013 May 15. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 23674099 Review.
References
-
- Sweadner K. J., Rael E. (2000) Genomics 68, 41–56 - PubMed
-
- Geering K. (2006) Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol 290, F241–F250 - PubMed
-
- Fuller W., Eaton P., Bell J. R., Shattock M. J. (2004) FASEB J. 18, 197–199 - PubMed
-
- Palmer C. J., Scott B. T., Jones L. R. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 11126–11130 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

