The adaptor function of TRAPPC2 in mammalian TRAPPs explains TRAPPC2-associated SEDT and TRAPPC9-associated congenital intellectual disability
- PMID: 21858081
- PMCID: PMC3156116
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023350
The adaptor function of TRAPPC2 in mammalian TRAPPs explains TRAPPC2-associated SEDT and TRAPPC9-associated congenital intellectual disability
Abstract
Background: The TRAPP (Transport protein particle) complex is a conserved protein complex functioning at various steps in vesicle transport. Although yeast has three functionally and structurally distinct forms, TRAPPI, II and III, emerging evidence suggests that mammalian TRAPP complex may be different. Mutations in the TRAPP complex subunit 2 (TRAPPC2) cause X-linked spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda, while mutations in the TRAPP complex subunit 9 (TRAPPC9) cause postnatal mental retardation with microcephaly. The structural interplay between these subunits found in mammalian equivalent of TRAPPI and those specific to TRAPPII and TRAPPIII remains largely unknown and we undertook the present study to examine the interaction between these subunits. Here, we reveal that the mammalian equivalent of the TRAPPII complex is structurally distinct from the yeast counterpart thus leading to insight into mechanism of disease.
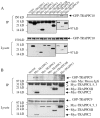
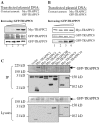
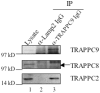
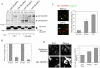
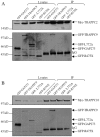
Principal findings: We analyzed how TRAPPII- or TRAPPIII- specific subunits interact with the six-subunit core complex of TRAPP by co-immunoprecipitation in mammalian cells. TRAPPC2 binds to TRAPPII-specific subunit TRAPPC9, which in turn binds to TRAPPC10. Unexpectedly, TRAPPC2 can also bind to the putative TRAPPIII-specific subunit, TRAPPC8. Endogenous TRAPPC9-positive TRAPPII complex does not contain TRAPPC8, suggesting that TRAPPC2 binds to either TRAPPC9 or TRAPPC8 during the formation of the mammalian equivalents of TRAPPII or TRAPPIII, respectively. Therefore, TRAPPC2 serves as an adaptor for the formation of these complexes. A disease-causing mutation of TRAPPC2, D47Y, failed to interact with either TRAPPC9 or TRAPPC8, suggesting that aspartate 47 in TRAPPC2 is at or near the site of interaction with TRAPPC9 or TRAPPC8, mediating the formation of TRAPPII and/or TRAPPIII. Furthermore, disease-causing deletional mutants of TRAPPC9 all failed to interact with TRAPPC2 and TRAPPC10.
Conclusions: TRAPPC2 serves as an adaptor for the formation of TRAPPII or TRAPPIII in mammalian cells. The mammalian equivalent of TRAPPII is likely different from the yeast TRAPPII structurally.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biochemical Insight into Novel Rab-GEF Activity of the Mammalian TRAPPIII Complex.J Mol Biol. 2021 Sep 3;433(18):167145. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167145. Epub 2021 Jul 3. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34229011
-
A trs20 mutation that mimics an SEDT-causing mutation blocks selective and non-selective autophagy: a model for TRAPP III organization.Traffic. 2013 Oct;14(10):1091-104. doi: 10.1111/tra.12095. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 23898804
-
Characterization of Aspergillus nidulans TRAPPs uncovers unprecedented similarities between fungi and metazoans and reveals the modular assembly of TRAPPII.PLoS Genet. 2019 Dec 23;15(12):e1008557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008557. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31869332 Free PMC article.
-
TRAPPC9: Novel insights into its trafficking and signaling pathways in health and disease (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2018 Dec;42(6):2991-2997. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3889. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30272317 Review.
-
In sickness and in health: the role of TRAPP and associated proteins in disease.Traffic. 2014 Aug;15(8):803-18. doi: 10.1111/tra.12183. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Traffic. 2014. PMID: 24917561 Review.
Cited by
-
Recessive TRAPPC11 mutations cause a disease spectrum of limb girdle muscular dystrophy and myopathy with movement disorder and intellectual disability.Am J Hum Genet. 2013 Jul 11;93(1):181-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.05.028. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Am J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23830518 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structure of metazoan TRAPPIII, the multi-subunit complex that activates the GTPase Rab1.EMBO J. 2021 Jun 15;40(12):e107608. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020107608. Epub 2021 May 21. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 34018214 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of TRAPPC9 and BAIAP2 Gene Polymorphisms and Their Association With Fat Deposition-Related Traits in Hu Sheep.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jul 5;9:928375. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.928375. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35865874 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for assembly of TRAPPII complex and specific activation of GTPase Ypt31/32.Sci Adv. 2022 Jan 28;8(4):eabi5603. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abi5603. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35080977 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of NIK/IKK2-binding protein (NIBP)/trafficking protein particle complex 9 (TRAPPC9) in nervous system diseases.Transl Res. 2020 Oct;224:55-70. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.05.001. Epub 2020 May 17. Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32434006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barrowman J, Bhandari D, Reinisch K, Ferro-Novick S. TRAPP complexes in membrane traffic: convergence through a common Rab. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:759–763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

