An R package implementation of multifactor dimensionality reduction
- PMID: 21846375
- PMCID: PMC3177775
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0381-4-24
An R package implementation of multifactor dimensionality reduction
Abstract
Background: A breadth of high-dimensional data is now available with unprecedented numbers of genetic markers and data-mining approaches to variable selection are increasingly being utilized to uncover associations, including potential gene-gene and gene-environment interactions. One of the most commonly used data-mining methods for case-control data is Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction (MDR), which has displayed success in both simulations and real data applications. Additional software applications in alternative programming languages can improve the availability and usefulness of the method for a broader range of users.
Results: We introduce a package for the R statistical language to implement the Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction (MDR) method for nonparametric variable selection of interactions. This package is designed to provide an alternative implementation for R users, with great flexibility and utility for both data analysis and research. The 'MDR' package is freely available online at http://www.r-project.org/. We also provide data examples to illustrate the use and functionality of the package.
Conclusions: MDR is a frequently-used data-mining method to identify potential gene-gene interactions, and alternative implementations will further increase this usage. We introduce a flexible software package for R users.
Figures
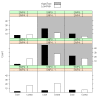
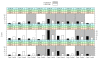
Similar articles
-
A roadmap to multifactor dimensionality reduction methods.Brief Bioinform. 2016 Mar;17(2):293-308. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv038. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Brief Bioinform. 2016. PMID: 26108231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of multifactor dimensionality reduction to genome-wide data using the R package 'MDR'.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1019:479-98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-447-0_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23756907
-
A unified model based multifactor dimensionality reduction framework for detecting gene-gene interactions.Bioinformatics. 2016 Sep 1;32(17):i605-i610. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw424. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27587680
-
The R-package GenomicTools for multifactor dimensionality reduction and the analysis of (exploratory) Quantitative Trait Loci.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017 Nov;151:171-177. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28946999
-
Gene-gene interaction: the curse of dimensionality.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Dec;7(24):813. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.12.87. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 32042829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comparison of internal model validation methods for multifactor dimensionality reduction in the case of genetic heterogeneity.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Nov 5;5:623. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-623. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 23126544 Free PMC article.
-
A roadmap to multifactor dimensionality reduction methods.Brief Bioinform. 2016 Mar;17(2):293-308. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv038. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Brief Bioinform. 2016. PMID: 26108231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Genetic Polymorphisms with Complications of Implanted LVAD Devices in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure: A Kazakhstani Study.J Pers Med. 2022 May 4;12(5):744. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050744. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35629166 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting epistasis in human complex traits.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Nov;15(11):722-33. doi: 10.1038/nrg3747. Epub 2014 Sep 9. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25200660 Review.
-
Association Mapping and Development of Marker-Assisted Selection Tools for the Resistance to White Pine Blister Rust in the Alberta Limber Pine Populations.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Sep 15;11:557672. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.557672. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33042181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moore JH. Detecting, characterizing, and interpreting nonlinear gene-gene interactions using multifactor dimensionality reduction. Adv Genet. 2010;72:101–116. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

