Mir-290-295 deficiency in mice results in partially penetrant embryonic lethality and germ cell defects
- PMID: 21844366
- PMCID: PMC3161528
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1111241108
Mir-290-295 deficiency in mice results in partially penetrant embryonic lethality and germ cell defects
Abstract
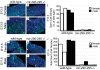
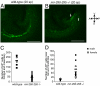
Mir-290 through mir-295 (mir-290-295) is a mammalian-specific microRNA (miRNA) cluster that, in mice, is expressed specifically in early embryos and embryonic germ cells. Here, we show that mir-290-295 plays important roles in embryonic development as indicated by the partially penetrant lethality of mutant embryos. In addition, we show that in surviving mir-290-295-deficient embryos, female but not male fertility is compromised. This impairment in fertility arises from a defect in migrating primordial germ cells and occurs equally in male and female mutant animals. Male mir-290-295(-/-) mice, due to the extended proliferative lifespan of their germ cells, are able to recover from this initial germ cell loss and are fertile. Female mir-290-295(-/-) mice are unable to recover and are sterile, due to premature ovarian failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential role of miR-29b in modulation of Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b expression in primordial germ cells of female mouse embryos.RNA. 2009 Aug;15(8):1507-14. doi: 10.1261/rna.1418309. Epub 2009 Jun 9. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19509302 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Apela Peptide in Mice Causes Low Penetrance Embryonic Lethality and Defects in Early Mesodermal Derivatives.Cell Rep. 2017 Aug 29;20(9):2116-2130. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.014. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28854362 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of the MiR-17-92 MicroRNA Cluster in Germ Cells Causes Subfertility in Female Mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(2):491-504. doi: 10.1159/000487028. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29402772
-
Heart defects and embryonic lethality in Asb2 knock out mice correlate with placental defects.Cells Dev. 2021 Mar;165:203663. doi: 10.1016/j.cdev.2021.203663. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Cells Dev. 2021. PMID: 33993984
-
Endocrine disrupters, microRNAs, and primordial germ cells: a dangerous cocktail.Fertil Steril. 2016 Sep 15;106(4):871-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.07.1100. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Fertil Steril. 2016. PMID: 27521771 Review.
Cited by
-
The Evolution of Imprinted microRNAs and Their RNA Targets.Genes (Basel). 2020 Sep 3;11(9):1038. doi: 10.3390/genes11091038. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32899179 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting microRNA-mediated regulation of stemness, reprogramming, and pluripotency.Cell Regen. 2016 Mar 22;5:2. doi: 10.1186/s13619-016-0028-0. eCollection 2016. Cell Regen. 2016. PMID: 27006752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Msx1 and Msx2 function together in the regulation of primordial germ cell migration in the mouse.Dev Biol. 2016 Sep 1;417(1):11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.07.013. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27435625 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: From Mechanism to Organism.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 3;8:409. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00409. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32582699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of stem cell populations by microRNAs.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;786:329-51. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-6621-1_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23696365 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5-F32-HD051190/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA14051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM034277/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01-HD045022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA42063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD045022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM34277/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R37CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01 CA042063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HD051190/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

