High-resolution description of antibody heavy-chain repertoires in humans
- PMID: 21829618
- PMCID: PMC3150326
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022365
High-resolution description of antibody heavy-chain repertoires in humans
Abstract
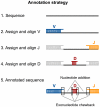
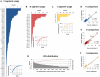
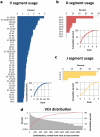
Antibodies' protective, pathological, and therapeutic properties result from their considerable diversity. This diversity is almost limitless in potential, but actual diversity is still poorly understood. Here we use deep sequencing to characterize the diversity of the heavy-chain CDR3 region, the most important contributor to antibody binding specificity, and the constituent V, D, and J segments that comprise it. We find that, during the stepwise D-J and then V-DJ recombination events, the choice of D and J segments exert some bias on each other; however, we find the choice of the V segment is essentially independent of both. V, D, and J segments are utilized with different frequencies, resulting in a highly skewed representation of VDJ combinations in the repertoire. Nevertheless, the pattern of segment usage was almost identical between two different individuals. The pattern of V, D, and J segment usage and recombination was insufficient to explain overlap that was observed between the two individuals' CDR3 repertoires. Finally, we find that while there are a near-infinite number of heavy-chain CDR3s in principle, there are about 3-9 million in the blood of an adult human being.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibody repertoire development in fetal and neonatal piglets. II. Characterization of heavy chain complementarity-determining region 3 diversity in the developing fetus.J Immunol. 2000 Dec 15;165(12):6999-7010. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.12.6999. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11120827
-
Expressed antibody repertoires in human cord blood cells: 454 sequencing and IMGT/HighV-QUEST analysis of germline gene usage, junctional diversity, and somatic mutations.Immunogenetics. 2012 May;64(5):337-50. doi: 10.1007/s00251-011-0595-8. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Immunogenetics. 2012. PMID: 22200891 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental changes in the human heavy chain CDR3.J Immunol. 2005 Dec 1;175(11):7425-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.11.7425. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16301650
-
Antibody repertoire development in swine.Dev Comp Immunol. 2006;30(1-2):199-221. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2005.06.025. Dev Comp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16168480 Review.
-
Diversification of Antibodies: From V(D)J Recombination to Somatic Exon Shuffling.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct;40(1):265-281. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-112122-030835. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39356809 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-to-cell expression dispersion of B-cell surface proteins is linked to genetic variants in humans.Commun Biol. 2020 Jul 3;3(1):346. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-1075-1. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32620900 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent antibody signatures in human dengue.Cell Host Microbe. 2013 Jun 12;13(6):691-700. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.05.008. Cell Host Microbe. 2013. PMID: 23768493 Free PMC article.
-
High Frequency of Shared Clonotypes in Human T Cell Receptor Repertoires.Cell Rep. 2020 Jul 14;32(2):107882. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107882. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32668251 Free PMC article.
-
Prize-based contests can provide solutions to computational biology problems.Nat Biotechnol. 2013 Feb;31(2):108-11. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2495. Nat Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23392504 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Deep Characterization of the Human Antibody Response to Natural Infection Using Longitudinal Immune Repertoire Sequencing.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Feb;19(2):278-293. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001633. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31767621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

