Redox-induced Src kinase and caveolin-1 signaling in TGF-β1-initiated SMAD2/3 activation and PAI-1 expression
- PMID: 21829547
- PMCID: PMC3145778
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022896
Redox-induced Src kinase and caveolin-1 signaling in TGF-β1-initiated SMAD2/3 activation and PAI-1 expression
Abstract
Background: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), a major regulator of the plasmin-based pericellular proteolytic cascade, is significantly increased in human arterial plaques contributing to vessel fibrosis, arteriosclerosis and thrombosis, particularly in the context of elevated tissue TGF-β1. Identification of molecular events underlying to PAI-1 induction in response to TGF-β1 may yield novel targets for the therapy of cardiovascular disease.
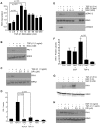
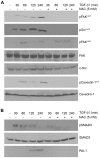
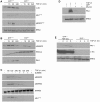
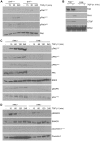
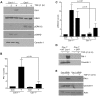
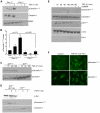
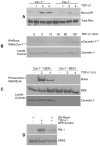
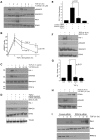
Principal findings: Reactive oxygen species are generated within 5 minutes after addition of TGF-β1 to quiescent vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) resulting in pp60(c-src) activation and PAI-1 expression. TGF-β1-stimulated Src kinase signaling sustained the duration (but not the initiation) of SMAD3 phosphorylation in VSMC by reducing the levels of PPM1A, a recently identified C-terminal SMAD2/3 phosphatase, thereby maintaining SMAD2/3 in an active state with retention of PAI-1 transcription. The markedly increased PPM1A levels in triple Src kinase (c-Src, Yes, Fyn)-null fibroblasts are consistent with reductions in both SMAD3 phosphorylation and PAI-1 expression in response to TGF-β1 compared to wild-type cells. Activation of the Rho-ROCK pathway was mediated by Src kinases and required for PAI-1 induction in TGF-β1-stimulated VSMCs. Inhibition of Rho-ROCK signaling blocked the TGF-β1-mediated decrease in nuclear PPM1A content and effectively attenuated PAI-1 expression. TGF-β1-induced PAI-1 expression was undetectable in caveolin-1-null cells, correlating with the reduced Rho-GTP loading and SMAD2/3 phosphorylation evident in TGF-β1-treated caveolin-1-deficient cells relative to their wild-type counterparts. Src kinases, moreover, were critical upstream effectors of caveolin-1(Y14) phosphoryation and initiation of downstream signaling.
Conclusions: TGF-β1-initiated Src-dependent caveolin-1(Y14) phosphorylation is a critical event in Rho-ROCK-mediated suppression of nuclear PPM1A levels maintaining, thereby, SMAD2/3-dependent transcription of the PAI-1 gene.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The TGF-β1/p53/PAI-1 Signaling Axis in Vascular Senescence: Role of Caveolin-1.Biomolecules. 2019 Aug 3;9(8):341. doi: 10.3390/biom9080341. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31382626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells requires pp60(c-src)/EGFR(Y845) and Rho/ROCK signaling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008 Mar;44(3):527-38. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.12.006. Epub 2008 Jan 3. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18255094 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression and induced migration in TGF-beta1-stimulated smooth muscle cells is pp60(c-src)/MEK-dependent.J Cell Physiol. 2005 Jul;204(1):236-46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20279. J Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15622520
-
Induction of renal fibrotic genes by TGF-β1 requires EGFR activation, p53 and reactive oxygen species.Cell Signal. 2013 Nov;25(11):2198-209. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23872073
-
Integration of non-SMAD and SMAD signaling in TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Dec;100(6):976-83. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 19132220 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 suppresses profibrotic responses in fibroblasts from fibrotic lungs.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9428-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.601815. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25648892 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of transforming growth factor β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells by c-Src kinase under high glucose conditions.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Aug;16(2):1520-1528. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6348. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30116401 Free PMC article.
-
The TGF-β1/p53/PAI-1 Signaling Axis in Vascular Senescence: Role of Caveolin-1.Biomolecules. 2019 Aug 3;9(8):341. doi: 10.3390/biom9080341. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31382626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus on liver fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smad pathway-mediated inhibition of extracellular matrix and autophagy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Feb 12;10:619-30. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S98740. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 26929597 Free PMC article.
-
PAI-1, the Plasminogen System, and Skeletal Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 25;21(19):7066. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197066. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32993026 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vaughan DE. PAI-1 and atherothrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:1879–1883. - PubMed
-
- Weisberg AD, Albornoz F, Griffin JP, Crandall DL, Elokdah H, et al. Pharmacological inhibition and genetic deficiency of PAI-1 attenuates angiotensin II/salt-induced aortic remodeling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:365–371. - PubMed
-
- Wang TJ, Gona P, Larson MG, Tofler GH, Levy D, et al. Multiple biomarkers for the prediction of first major cardiovascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2631–2639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

