Type 2 diabetes is associated with reduced ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 gene expression, protein and function
- PMID: 21829447
- PMCID: PMC3144880
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022142
Type 2 diabetes is associated with reduced ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 gene expression, protein and function
Abstract
Objective: Increasing plasma glucose levels are associated with increasing risk of vascular disease. We tested the hypothesis that there is a glycaemia-mediated impairment of reverse cholesterol transport (RCT). We studied the influence of plasma glucose on expression and function of a key mediator in RCT, the ATP binding cassette transporter-A1 (ABCA1) and expression of its regulators, liver X receptor-α (LXRα) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ).
Methods and results: Leukocyte ABCA1, LXRα and PPARγ expression was measured by polymerase chain reaction in 63 men with varying degrees of glucose homeostasis. ABCA1 protein concentrations were measured in leukocytes. In a sub-group of 25 men, ABCA1 function was quantified as apolipoprotein-A1-mediated cholesterol efflux from 2-3 week cultured skin fibroblasts. Leukocyte ABCA1 expression correlated negatively with circulating HbA1c and glucose (rho = -0.41, p<0.001; rho = -0.34, p = 0.006 respectively) and was reduced in Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) (p = 0.03). Leukocyte ABCA1 protein was lower in T2DM (p = 0.03) and positively associated with plasma HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) (rho = 0.34, p = 0.02). Apolipoprotein-A1-mediated cholesterol efflux correlated negatively with fasting glucose (rho = -0.50, p = 0.01) and positively with HDL-C (rho = 0.41, p = 0.02). It was reduced in T2DM compared with controls (p = 0.04). These relationships were independent of LXRα and PPARγ expression.
Conclusions: ABCA1 expression and protein concentrations in leukocytes, as well as function in cultured skin fibroblasts, are reduced in T2DM. ABCA1 protein concentration and function are associated with HDL-C levels. These findings indicate a glycaemia-related, persistent disruption of a key component of RCT.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
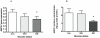
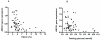
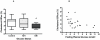
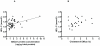
Similar articles
-
Quercetin up-regulates expressions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, liver X receptor α, and ATP binding cassette transporter A1 genes and increases cholesterol efflux in human macrophage cell line.Nutr Res. 2013 Feb;33(2):136-43. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2012.11.010. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Nutr Res. 2013. PMID: 23399664
-
Propofol up-regulates expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, and SR-B1 through the PPARγ/LXRα signaling pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells.Cardiovasc Pathol. 2015 Jul-Aug;24(4):230-5. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2014.12.004. Epub 2014 Dec 27. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25600616
-
Niacin promotes cholesterol efflux through stimulation of the PPARgamma-LXRalpha-ABCA1 pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Pharmacology. 2009;84(5):282-7. doi: 10.1159/000242999. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Pharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19797938
-
ABCA1 and atherosclerosis.Vasc Med. 2005 May;10(2):109-19. doi: 10.1191/1358863x05vm593ra. Vasc Med. 2005. PMID: 16013195 Review.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 and HDL metabolism: effects of fatty acids.J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Jan;23(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Jun 17. J Nutr Biochem. 2012. PMID: 21684139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Rope Training on Lymphocyte ABCA1 Expression, Plasma ApoA-I and HDL-c in Boy Adolescents.Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Spring;11(2):76-81. doi: 10.5812/ijem.8178. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23825977 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc transporters, mechanisms of action and therapeutic utility: implications for type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Nutr Metab. 2012;2012:173712. doi: 10.1155/2012/173712. Epub 2012 Dec 12. J Nutr Metab. 2012. PMID: 23304467 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of microRNA Expression in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome and Decrease of Cholesterol Efflux from Macrophages via microRNA-33-Mediated Attenuation of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 Expression by Statins.PLoS One. 2016 May 3;11(5):e0154672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154672. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27139226 Free PMC article.
-
Tachometer for reverse cholesterol transport?J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Aug;1(4):e003723. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.112.003723. Epub 2012 Aug 24. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012. PMID: 23130178 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Hematopoietic Progenitors and the Bone Marrow Niche Shape the Inflammatory Response and Contribute to Chronic Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 17;23(4):2234. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042234. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eschwege E, Richard JL, Thibult N, Ducimetiere P, Warnet JM, et al. Coronary heart disease mortality in relation with diabetes, blood glucose and plasma insulin levels. The Paris Prospective Study, ten years later. Horm Metab. 1985;Res(Suppl 15):41–46. - PubMed
-
- Yan SF, Ramasamy R, Naka Y, Schmidt AM. Glycation, Inflammation, and RAGE: A Scaffold for the Macrovascular Complications of Diabetes and Beyond. Circ Res. 2003;93:1159–1169. - PubMed
-
- Krentz A. Lipoprotein abnormalities and their consequences for patients with Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism. 2003;5:s19. - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi Y, Chang CC, Hayashi M, be-Dohmae S, Reid PC, et al. Intracellular cholesterol mobilization involved in the ABCA1/apolipoprotein-mediated assembly of high density lipoprotein in fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:1943–1951. - PubMed

