EBV latency types adopt alternative chromatin conformations
- PMID: 21829357
- PMCID: PMC3145795
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002180
EBV latency types adopt alternative chromatin conformations
Abstract
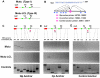
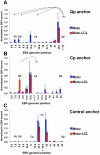
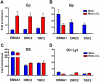
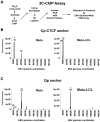
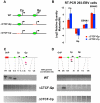
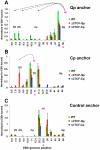
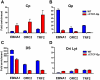
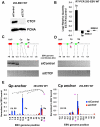
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) can establish latent infections with distinct gene expression patterns referred to as latency types. These different latency types are epigenetically stable and correspond to different promoter utilization. Here we explore the three-dimensional conformations of the EBV genome in different latency types. We employed Chromosome Conformation Capture (3C) assay to investigate chromatin loop formation between the OriP enhancer and the promoters that determine type I (Qp) or type III (Cp) gene expression. We show that OriP is in close physical proximity to Qp in type I latency, and to Cp in type III latency. The cellular chromatin insulator and boundary factor CTCF was implicated in EBV chromatin loop formation. Combining 3C and ChIP assays we found that CTCF is physically associated with OriP-Qp loop formation in type I and OriP-Cp loop formation in type III latency. Mutations in the CTCF binding site located at Qp disrupt loop formation between Qp and OriP, and lead to the activation of Cp transcription. Mutation of the CTCF binding site at Cp, as well as siRNA depletion of CTCF eliminates both OriP-associated loops, indicating that CTCF plays an integral role in loop formation. These data indicate that epigenetically stable EBV latency types adopt distinct chromatin architectures that depend on CTCF and mediate alternative promoter targeting by the OriP enhancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CTCF prevents the epigenetic drift of EBV latency promoter Qp.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Aug 12;6(8):e1001048. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001048. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20730088 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Epstein-Barr virus latency type by the chromatin boundary factor CTCF.J Virol. 2006 Jun;80(12):5723-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00025-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16731911 Free PMC article.
-
PARP1 Stabilizes CTCF Binding and Chromatin Structure To Maintain Epstein-Barr Virus Latency Type.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00755-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00755-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29976663 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of latent Epstein-Barr virus promoters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Mar-Apr;1799(3-4):228-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.10.005. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19853674 Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of EBV persistence and oncogenesis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Jun;26:22-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24468737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interpreting the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) epigenome using high-throughput data.Viruses. 2013 Apr 2;5(4):1042-54. doi: 10.3390/v5041042. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23549386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactivation of Epstein-Barr Virus from Latency Involves Increased RNA Polymerase Activity at CTCF Binding Sites on the Viral Genome.J Virol. 2023 Feb 28;97(2):e0189422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01894-22. Epub 2023 Feb 6. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36744959 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Synergizes with BRD7 to Conquer c-Myc-Mediated Viral Latency Maintenance via Chromatin Remodeling.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 2;11(2):e0123722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01237-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36728436 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr Virus Oncogene EBNA1 Suppresses Natural Killer Cell Responses and Apoptosis Early after Infection of Peripheral B Cells.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0224321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02243-21. Epub 2021 Nov 16. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34781735 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic specifications of host chromosome docking sites for latent Epstein-Barr virus.Nat Commun. 2020 Feb 13;11(1):877. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14152-8. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32054837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kieff E. Epstein-Barr Virus and its replication.; In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. 2 v. (xix, 3091, 3086 p.)
-
- Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr Virus.; In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. 2 v. (xix, 3091, 3086 p.)
-
- Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:757–768. - PubMed
-
- Miyashita EM, Yang B, Lam KM, Crawford DH, Thorley-Lawson DA. A novel form of Epstein-Barr virus latency in normal B cells in vivo. Cell. 1995;80:593–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

