Mutual regulation between deubiquitinase CYLD and retroviral oncoprotein Tax
- PMID: 21824392
- PMCID: PMC3170579
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-3701-1-27
Mutual regulation between deubiquitinase CYLD and retroviral oncoprotein Tax
Abstract
Background: Oncoprotein Tax, encoded by the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV1), persistently induces NF-κB activation, which contributes to HTLV1-mediated T-cell transformation. Recent studies suggest that the signaling function of Tax requires its ubiquitination, although how the Tax ubiquitination is regulated remains unclear.
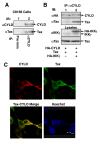
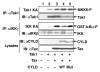
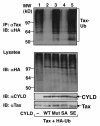
Results: We show here that the deubiquitinase CYLD physically interacts with Tax and negatively regulates the ubiquitination of this viral protein. This function of CYLD is associated with inhibition of Tax-mediated activation of IKK although not that of Tak1. Interestingly, CYLD undergoes constitutive phosphorylation in HTLV1-transformed T cells, a mechanism known to inactivate the catalytic activity of CYLD. Consistently, a phospho-mimetic CYLD mutant fails to inhibit Tax ubiquitination.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that CYLD negatively regulates the signaling function of Tax through inhibition of Tax ubiquitination. Conversely, induction of CYLD phosphorylation may serve as a mechanism by which HTLV1 overrides the inhibitory function of CYLD, leading to the persistent activation of NF-κB.
Figures
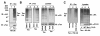
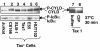
Similar articles
-
Retroviral oncoprotein Tax deregulates NF-kappaB by activating Tak1 and mediating the physical association of Tak1-IKK.EMBO Rep. 2007 May;8(5):510-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400931. Epub 2007 Mar 16. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17363973 Free PMC article.
-
The tax oncoprotein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 associates with and persistently activates IkappaB kinases containing IKKalpha and IKKbeta.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 26;273(26):15891-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.26.15891. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9632633
-
Activation of I-kappaB kinase by the HTLV type 1 Tax protein: mechanistic insights into the adaptor function of IKKgamma.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Nov 1;16(16):1591-6. doi: 10.1089/08892220050193001. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 11080796 Review.
-
IKKgamma serves as a docking subunit of the IkappaB kinase (IKK) and mediates interaction of IKK with the human T-cell leukemia virus Tax protein.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 13;274(33):22911-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.33.22911. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10438454
-
Activation of NF-kappaB by HTLV-I and implications for cell transformation.Oncogene. 2005 Sep 5;24(39):5952-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208969. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16155602 Review.
Cited by
-
NF-κB and MicroRNA Deregulation Mediated by HTLV-1 Tax and HBZ.Pathogens. 2019 Dec 10;8(4):290. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040290. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31835460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-kappaB activation: Tax sumoylation is out, but what about Tax ubiquitination?Retrovirology. 2012 Sep 25;9:78. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-9-78. Retrovirology. 2012. PMID: 23009565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal of CYLD phosphorylation as a novel therapeutic approach for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL).Cell Death Dis. 2020 Feb 5;11(2):94. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2294-6. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32024820 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV tax: a fascinating multifunctional co-regulator of viral and cellular pathways.Front Microbiol. 2012 Nov 30;3:406. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00406. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23226145 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) tax requires CADM1/TSLC1 for inactivation of the NF-κB inhibitor A20 and constitutive NF-κB signaling.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Mar 16;11(3):e1004721. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004721. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25774694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shuh M, Beilke M. The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1): new insights into the clinical aspects and molecular pathogenesis of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) and tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-associated myelopathy (TSP/HAM) Microsc Res Tech. 2005;68:176–196. doi: 10.1002/jemt.20231. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

