A resource of vectors and ES cells for targeted deletion of microRNAs in mice
- PMID: 21822254
- PMCID: PMC3242032
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1929
A resource of vectors and ES cells for targeted deletion of microRNAs in mice
Abstract
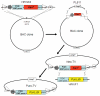
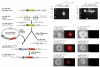
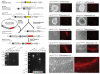
The 21-23 nucleotide, single-stranded RNAs classified as microRNAs (miRNA) perform fundamental roles in diverse cellular and developmental processes. In contrast to the situation for protein-coding genes, no public resource of miRNA mouse mutant alleles exists. Here we describe a collection of 428 miRNA targeting vectors covering 476 of the miRNA genes annotated in the miRBase registry. Using these vectors, we generated a library of highly germline-transmissible C57BL/6N mouse embryonic stem (ES) cell clones harboring targeted deletions for 392 miRNA genes. For most of these targeted clones, chimerism and germline transmission can be scored through a coat color marker. The targeted alleles have been designed to be adaptable research tools that can be efficiently altered by recombinase-mediated cassette exchange to create reporter, conditional and other allelic variants. This miRNA knockout (mirKO) resource can be searched electronically and is available from ES cell repositories for distribution to the scientific community.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficient generation of long-distance conditional alleles using recombineering and a dual selection strategy in replicate plates.BMC Biotechnol. 2009 Jul 28;9:69. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-9-69. BMC Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19638212 Free PMC article.
-
A conditional knockout resource for the genome-wide study of mouse gene function.Nature. 2011 Jun 15;474(7351):337-42. doi: 10.1038/nature10163. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21677750 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Insertion of loxP Sites in the Mouse Dock7 Gene Provides an Effective Alternative to Use of Targeted Embryonic Stem Cells.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Jul 7;6(7):2051-61. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.030601. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27175020 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review.
-
Emerging roles of microRNAs in the control of embryonic stem cells and the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells.Dev Biol. 2010 Aug 1;344(1):16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.05.014. Epub 2010 May 15. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20478297 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the p53/microRNA Network in Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1385:187-228. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08356-3_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36352215 Review.
-
MicroRNA-mediated regulation of T helper cell differentiation and plasticity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Sep;13(9):666-78. doi: 10.1038/nri3494. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23907446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Independent regulation of vertebral number and vertebral identity by microRNA-196 paralogs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 1;112(35):E4884-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512655112. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26283362 Free PMC article.
-
miR-29 is an important driver of aging-related phenotypes.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 27;7(1):1055. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06735-z. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39191864 Free PMC article.
-
Site specific mutation of the Zic2 locus by microinjection of TALEN mRNA in mouse CD1, C3H and C57BL/6J oocytes.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060216. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555929 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

