Ribosomal protein L11 recruits miR-24/miRISC to repress c-Myc expression in response to ribosomal stress
- PMID: 21807902
- PMCID: PMC3187350
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.05810-11
Ribosomal protein L11 recruits miR-24/miRISC to repress c-Myc expression in response to ribosomal stress
Abstract
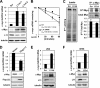
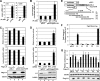
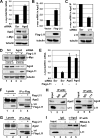
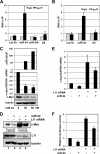
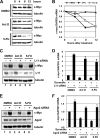
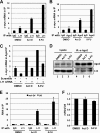
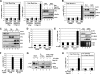
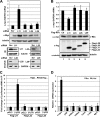
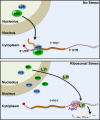
c-Myc promotes cell growth by enhancing ribosomal biogenesis and translation. Deregulated expression of c-Myc and aberrant ribosomal biogenesis and translation contribute to tumorigenesis. Thus, a fine coordination between c-Myc and ribosomal biogenesis is vital for normal cell homeostasis. Here, we show that ribosomal protein L11 regulates c-myc mRNA turnover. L11 binds to c-myc mRNA at its 3' untranslated region (3'-UTR), the core component of microRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) argonaute 2 (Ago2), as well as miR-24, leading to c-myc mRNA reduction. Knockdown of L11 drastically increases the levels and stability of c-myc mRNA. Ablation of Ago2 abrogated the L11-mediated reduction of c-myc mRNA, whereas knockdown of L11 rescued miR-24-mediated c-myc mRNA decay. Interestingly, treatment of cells with the ribosomal stress-inducing agent actinomycin D or 5-fluorouracil significantly decreased the c-myc mRNA levels in an L11- and Ago2-dependent manner. Both treatments enhanced the association of L11 with Ago2, miR-24, and c-myc mRNA. We further show that ribosome-free L11 binds to c-myc mRNA in the cytoplasm and that this binding is enhanced by actinomycin D treatment. Together, our results identify a novel regulatory paradigm wherein L11 plays a critical role in controlling c-myc mRNA turnover via recruiting miRISC in response to ribosomal stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-130a associates with ribosomal protein L11 to suppress c-Myc expression in response to UV irradiation.Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 20;6(2):1101-14. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2728. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25544755 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal protein L11 associates with c-Myc at 5 S rRNA and tRNA genes and regulates their expression.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 23;285(17):12587-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.056259. Epub 2010 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20194507 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal proteins L5 and L11 co-operatively inactivate c-Myc via RNA-induced silencing complex.Oncogene. 2014 Oct 9;33(41):4916-23. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.430. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24141778 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback regulation of c-Myc by ribosomal protein L11.Cell Cycle. 2007 Nov 15;6(22):2735-41. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.22.4895. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 18032916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MYC as a regulator of ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Apr;10(4):301-9. doi: 10.1038/nrc2819. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20332779 Review.
Cited by
-
5S ribosomal RNA is an essential component of a nascent ribosomal precursor complex that regulates the Hdm2-p53 checkpoint.Cell Rep. 2013 Jul 11;4(1):87-98. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.05.045. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23831031 Free PMC article.
-
p53 -Dependent and -Independent Nucleolar Stress Responses.Cells. 2012 Oct 15;1(4):774-98. doi: 10.3390/cells1040774. Cells. 2012. PMID: 24710530 Free PMC article.
-
Compensation between Wnt-driven tumorigenesis and cellular responses to ribosome biogenesis inhibition in the murine intestinal epithelium.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Oct;27(10):2872-2887. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0548-6. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 32355182 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal proteins and human diseases: molecular mechanisms and targeted therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Aug 30;6(1):323. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00728-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34462428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-24-mediated knockdown of H2AX damages mitochondria and the insulin signaling pathway.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Apr 7;49(4):e313. doi: 10.1038/emm.2016.174. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28386126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhikary S., Eilers M. 2005. Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6:635–645 - PubMed
-
- Andersen J. S., et al. 2002. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr. Biol. 12:1–11 - PubMed
-
- Arabi A., et al. 2005. c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat. Cell Biol. 7:303–310 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya S. N., Habermacher R., Martine U., Closs E. I., Filipowicz W. 2006. Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell 125:1111–1124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
