Enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 3C proteases: binding to rupintrivir and their substrates and anti-hand, foot, and mouth disease virus drug design
- PMID: 21795339
- PMCID: PMC3196414
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00787-11
Enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 3C proteases: binding to rupintrivir and their substrates and anti-hand, foot, and mouth disease virus drug design
Abstract
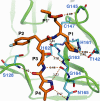
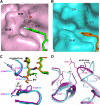
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) and coxsackievirus A16 (CVA16) are the major causative agents of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), which is prevalent in Asia. Thus far, there are no prophylactic or therapeutic measures against HFMD. The 3C proteases from EV71 and CVA16 play important roles in viral replication and are therefore ideal drug targets. By using biochemical, mutational, and structural approaches, we broadly characterized both proteases. A series of high-resolution structures of the free or substrate-bound enzymes were solved. These structures, together with our cleavage specificity assay, well explain the marked substrate preferences of both proteases for particular P4, P1, and P1' residue types, as well as the relative malleability of the P2 amino acid. More importantly, the complex structures of EV71 and CVA16 3Cs with rupintrivir, a specific human rhinovirus (HRV) 3C protease inhibitor, were solved. These structures reveal a half-closed S2 subsite and a size-reduced S1' subsite that limit the access of the P1' group of rupintrivir to both enzymes, explaining the reported low inhibition activity of the compound toward EV71 and CVA16. In conclusion, the detailed characterization of both proteases in this study could direct us to a proposal for rational design of EV71/CVA16 3C inhibitors.
Figures
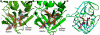
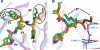
Similar articles
-
Crystal structures of enterovirus 71 3C protease complexed with rupintrivir reveal the roles of catalytically important residues.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):10021-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05107-11. Epub 2011 Aug 3. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21813612 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of Enterovirus 71 3C proteinase (strain E2004104-TW-CDC) and its complex with rupintrivir.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 May;69(Pt 5):866-71. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913002862. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23633597
-
Structure of the Enterovirus 71 3C Protease in Complex with NK-1.8k and Indications for the Development of Antienterovirus Protease Inhibitor.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jun 27;61(7):e00298-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00298-17. Print 2017 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28461310 Free PMC article.
-
An update on enterovirus 71 infection and interferon type I response.Rev Med Virol. 2019 Jan;29(1):e2016. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2016. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Rev Med Virol. 2019. PMID: 30378208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Function and Mechanism of Enterovirus 71 (EV71) 3C Protease.Curr Microbiol. 2020 Sep;77(9):1968-1975. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-02082-4. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Curr Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32556480 Review.
Cited by
-
The Pathogenesis and Prevention of Encephalitis due to Human Enterovirus 71.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2012 Aug;14(4):397-407. doi: 10.1007/s11908-012-0267-3. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2012. PMID: 22639066
-
Enterovirus 71 infection and vaccines.Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2017 Jan;6(1):4-14. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2017.6.1.4. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2017. PMID: 28168168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DWV Infection in vitro Using Honey Bee Pupal Tissue.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 10;12:631889. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.631889. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33643262 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-Aided Prediction of the Interactions of Viral Proteases with Antiviral Drugs: Antiviral Potential of Broad-Spectrum Drugs.Molecules. 2023 Dec 31;29(1):225. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010225. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202808 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the treatment of virus-induced asthma.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016 Jun;10(6):629-41. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2016.1180249. Epub 2016 May 3. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016. PMID: 27088397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander J. P., Jr., Baden L., Pallansch M. A., Anderson L. J. 1994. Enterovirus 71 infections and neurologic disease—United States, 1977–1991. J. Infect. Dis. 169:905–908 - PubMed
-
- Berger A., Schechter I. 1970. Mapping the active site of papain with the aid of peptide substrates and inhibitors. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 257:249–264 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

