Neutrophil clearance: when the party is over, clean-up begins
- PMID: 21782511
- PMCID: PMC3151332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2011.04.009
Neutrophil clearance: when the party is over, clean-up begins
Abstract
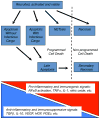
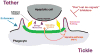
Maintenance of circulating, functional neutrophils and their robust recruitment to tissues in response to injury and/or microbial infection are crucial for host defense. Equally important, although less well understood, are the processes for removal of these short-lived cells. Here, we review recent findings of novel neutrophil characteristics that determine removal. These neutrophil-derived signals, in turn, can shape the responses of other cells and surrounding tissues and promote a return to homeostasis. If not removed, dying neutrophils disintegrate and release phlogistic cargo that can further contribute to ongoing inflammation, tissue destruction, or autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction of Neutrophils with Macrophages Promotes IL-1β Maturation and Contributes to Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.J Immunol. 2017 Nov 1;199(9):3306-3315. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700717. Epub 2017 Oct 2. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28972095
-
The neutrophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007 May;119(5):1065-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.12.640. Epub 2007 Jan 30. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17270263 Review.
-
An essential role for IL-17 in preventing pathogen-initiated bone destruction: recruitment of neutrophils to inflamed bone requires IL-17 receptor-dependent signals.Blood. 2007 May 1;109(9):3794-802. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-09-010116. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17202320 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette smoke-exposed neutrophils die unconventionally but are rapidly phagocytosed by macrophages.Cell Death Dis. 2011 Mar 17;2(3):e131. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.13. Cell Death Dis. 2011. PMID: 21412277 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neutrophil apoptosis in the resolution of inflammation.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Sep 1;10:1731-48. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.169. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 20842319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ADAMTS-12 metalloprotease is necessary for normal inflammatory response.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 16;287(47):39554-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.408625. Epub 2012 Sep 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23019333 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets orchestrate the resolution of pulmonary inflammation in mice by T reg cell repositioning and macrophage education.J Exp Med. 2021 Jul 5;218(7):e20201353. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201353. Epub 2021 May 20. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34014253 Free PMC article.
-
Whole blood human neutrophil trafficking in a microfluidic model of infection and inflammation.Lab Chip. 2015 Jun 21;15(12):2625-33. doi: 10.1039/c5lc00245a. Lab Chip. 2015. PMID: 25987163 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil cell death in response to infection and its relation to coagulation.J Intensive Care. 2013 Dec 4;1(1):13. doi: 10.1186/2052-0492-1-13. eCollection 2013. J Intensive Care. 2013. PMID: 25705405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Centella asiatica extract in carboxymethyl cellulose at its optimal concentration improved wound healing in mice model.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 5;8(12):e12031. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12031. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. Retraction in: Heliyon. 2023 Jul 27;9(8):e18722. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18722. PMID: 36531634 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Nathan C. Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:173–182. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy AD, DeLeo FR. Neutrophil apoptosis and the resolution of infection. Immunol Res. 2009;43:25–61. - PubMed
-
- Pillay J, et al. In vivo labeling with 2H2O reveals a human neutrophil lifespan of 5.4 days. Blood. 2010;116:625–627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL068864-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL034303-20/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081151-07/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL68864/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL34303/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068864/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM061031/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM61031/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM061031-08/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL81151/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081151/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL034303/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

